Association between the XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphisms and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24802942
- PMCID: PMC4011698
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088490
Association between the XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphisms and risk of cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The XPG (xeroderma pigmentosum type G) Asp1104His and XPF (xeroderma pigmentosum type F) Arg415Gln polymorphisms had been implicated in cancer susceptibility. The previous published data on the association between XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphisms and cancer risk remained controversial.
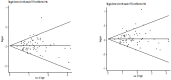
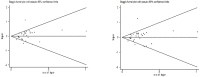
Methodology/principal findings: To derive a more precise estimation of the association between the XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphisms and overall cancer risk, we performed a meta-analysis to investigate the association between cancer susceptibility and XPG Asp1104His (32,162 cases and 39,858 controls from 66 studies) and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphisms (17,864 cases and 20,578 controls from 32 studies) in different inheritance models. We used odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals to assess the strength of the association. Overall, significantly elevated cancer risk was found when all studies were pooled into the meta-analysis of XPG Asp1104His (dominant model: OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.00-1.10; Asp/His vs. Asp/Asp: OR = 1.06, 95% CI = 1.01-1.11). In the further stratified and sensitivity analyses, significantly decreased lung cancer risk was found for XPF Arg415Gln (dominant model: OR = 0.82, 95% CI = 0.71-0.96; Arg/Gln versus Arg/Arg: OR = 0.83, 95% CI = 0.71-0.97; additive model: OR = 0.83, 95% CI = 0.72-0.95) and significantly increased other cancer risk was found among hospital-based studies for XPG Asp1104His (dominant model: OR = 1.23, 95% CI = 1.02-1.49).
Conclusions/significance: In summary, this meta-analysis suggests that XPF Arg415Gln polymorphism may be associated with decreased lung cancer risk and XPG Asp1104His may be a low-penetrant risk factor in some cancers development. And larger scale primary studies are required to further evaluate the interaction of XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphisms and cancer risk in specific populations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lack of association between XPG Asp1104His and XPF Arg415Gln polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis of case-control studies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Aug;129(1):203-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1447-9. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21424776
-
Genetic Association between the XPG Asp1104His Polymorphism and Head and Neck Cancer Susceptibility: Evidence Based on a Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(9):3645-51. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.9.3645. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25987016
-
Association between the XPG gene Asp1104His polymorphism and lung cancer risk.Genet Mol Res. 2016 Jun 10;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15027395. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27323149
-
Association of XPG rs17655G>C and XPF rs1799801T>C Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma: Evidence from a Case-Control Study, Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Klin Onkol. 2020 Spring;33(3):184-194. doi: 10.14735/amko2020184. Klin Onkol. 2020. PMID: 32683874 English.
-
Quantitative assessment of the association between XPG Asp1104His polymorphism and bladder cancer risk.Tumour Biol. 2014 Feb;35(2):1203-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1161-9. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24061640 Review.
Cited by
-
XPC Ala499Val and XPG Asp1104His polymorphisms and digestive system cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on model-free approach.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):6621-30. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131294 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of XPC, XPD, XPF, and XPG gene polymorphisms on the risk and the outcome of acute myeloid leukemia in a Romanian population.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):9357-66. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4815-6. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26779634
-
Allele and genotype distributions of DNA repair gene polymorphisms in South Indian healthy population.Biomark Cancer. 2014 Dec 7;6:29-35. doi: 10.4137/BIC.S19681. eCollection 2014. Biomark Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25520562 Free PMC article.
-
CometChip enables parallel analysis of multiple DNA repair activities.DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Oct;106:103176. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103176. Epub 2021 Jul 10. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34365116 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of XPG rs2296147T>C polymorphism on clinical outcomes of cancer patients.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65770-65781. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11664. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27588464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wood RD, Mitchell M, Sgouros J, Lindahl T (2001) Human DNA repair genes. Science 291: 1284–1289. - PubMed
-
- Friedberg EC (2001) How nucleotide excision repair protects against cancer. Nature Rev Cancer 1: 22–33. - PubMed
-
- Cleaver JE (2000) Common pathways for ultraviolet skin carcinogenesis in the repair and replication defective groups of xeroderma pigmentosum. J Dermatol Sci 23: 1–11. - PubMed
-
- O'Donovan A, Davies AA, Moggs JG, West SC, Wood RD (1994) XPG endonuclease makes the 30 incision in human DNA nucleotide excision repair. Nature 371: 432–435. - PubMed
-
- Wakasugi M, Reardon JT, Sancar A (1997) The non-catalytic function of XPG protein during dual incision in human nucleotide excision repair. J Biol Chem 272: 16030–16034. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

