Focusing the amyloid cascade hypothesis on N-truncated Abeta peptides as drug targets against Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24803226
- PMCID: PMC4024135
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-014-1287-x
Focusing the amyloid cascade hypothesis on N-truncated Abeta peptides as drug targets against Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
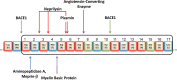
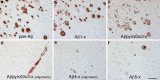
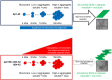
Although N-truncated Aβ variants are known to be the main constituent of amyloid plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease, their potential as targets for pharmacological intervention has only recently been investigated. In the last few years, the Alzheimer field has experienced a paradigm shift with the ever increasing understanding that targeting amyloid plaques has not led to a successful immunotherapy. On the other hand, there can be no doubt that the amyloid cascade hypothesis is central to the etiology of Alzheimer's disease, raising the question as to why it is apparently failing to translate into the clinic. In this review, we aim to refocus the amyloid hypothesis integrating N-truncated Aβ peptides based on mounting evidence that they may represent better targets than full-length Aβ. In addition to Aβ peptides starting with an Asp at position 1, a variety of different N-truncated Aβ peptides have been identified starting with amino residue Ala-2, pyroglutamylated Glu-3, Phe-4, Arg-5, His-6, Asp-7, Ser-8, Gly-9, Tyr-10 and pyroglutamylated Glu-11. Certain forms of N-truncated species are better correlates for early pathological changes found pre-symptomatically more often than others. There is also evidence that, together with full-length Aβ, they might be physiologically detectable and are naturally secreted by neurons. Others are known to form soluble aggregates, which have neurotoxic properties in transgenic mouse models. It has been clearly demonstrated by several groups that some N-truncated Aβs dominate full-length Aβ in the brains of Alzheimer's patients. We try to address which of the N-truncated variants may be promising therapeutic targets and which enzymes might be involved in the generation of these peptides.
Figures
References
-
- Alexandru A, Jagla W, Graubner S, Becker A, Bäuscher C, Kohlmann S, Sedlmeier R, Raber KA, Cynis H, Rönicke R, Reymann KG, Petrasch-Parwez E, Hartlage-Rübsamen M, Waniek A, Rossner S, Schilling S, Osmand AP, Demuth H-U, von Hörsten S. Selective hippocampal neurodegeneration in transgenic mice expressing small amounts of truncated Aβ is induced by pyroglutamate-Aβ formation. J Neurosci. 2011;31:12790–12801. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ancolio K, Dumanchin C, Barelli H, Warter JM, Brice A, Campion D, Frebourg T, Checler F. Unusual phenotypic alteration of beta amyloid precursor protein (betaAPP) maturation by a new Val715Met betaAPP-770 mutation responsible for probable early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:4119–4124. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonios G, Saiepour N, Bouter Y, Richard BC, Paetau A, Verkkoniemi-Ahola A, Lannfelt L, Ingelsson M, Kovacs GG, Pillot T, Wirths O, Bayer TA. N-truncated Abeta starting with position four: early intraneuronal accumulation and rescue of toxicity using NT4X-167, a novel monoclonal antibody. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2013;1:56. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Nguyen M, Soriano F, Vasquez N, Weiss K, Welch B, Seubert P, Schenk D, Yednock T. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med. 2000;6:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Benilova I, Karran E, De Strooper B. The toxic Abeta oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;29:349–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

