Manipulation of BK channel expression is sufficient to alter auditory hair cell thresholds in larval zebrafish
- PMID: 24803460
- PMCID: PMC4103636
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.103093
Manipulation of BK channel expression is sufficient to alter auditory hair cell thresholds in larval zebrafish
Abstract
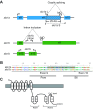
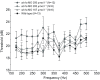
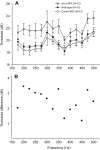
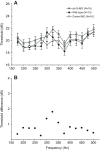
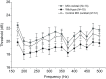
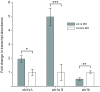
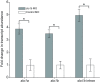
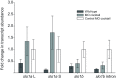
Non-mammalian vertebrates rely on electrical resonance for frequency tuning in auditory hair cells. A key component of the resonance exhibited by these cells is an outward calcium-activated potassium current that flows through large-conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels. Previous work in midshipman fish (Porichthys notatus) has shown that BK expression correlates with seasonal changes in hearing sensitivity and that pharmacologically blocking these channels replicates the natural decreases in sensitivity during the winter non-reproductive season. To test the hypothesis that reducing BK channel function is sufficient to change auditory thresholds in fish, morpholino oligonucleotides (MOs) were used in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) to alter expression of slo1a and slo1b, duplicate genes coding for the pore-forming α-subunits of BK channels. Following MO injection, microphonic potentials were recorded from the inner ear of larvae. Quantitative real-time PCR was then used to determine the MO effect on slo1a and slo1b expression in these same fish. Knockdown of either slo1a or slo1b resulted in disrupted gene expression and increased auditory thresholds across the same range of frequencies of natural auditory plasticity observed in midshipman. We conclude that interference with the normal expression of individual slo1 genes is sufficient to increase auditory thresholds in zebrafish larvae and that changes in BK channel expression are a direct mechanism for regulation of peripheral hearing sensitivity among fishes.
Keywords: Auditory thresholds; Hair cell; Potassium channels; Saccule.
© 2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Seasonal plasticity of auditory saccular sensitivity in the vocal plainfin midshipman fish, Porichthys notatus.J Neurophysiol. 2009 Aug;102(2):1121-31. doi: 10.1152/jn.00236.2009. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19553489
-
Noise-induced hearing loss correlates with inner ear hair cell decrease in larval zebrafish.J Exp Biol. 2022 Apr 1;225(7):jeb243743. doi: 10.1242/jeb.243743. Epub 2022 Apr 6. J Exp Biol. 2022. PMID: 35258623
-
Calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels are encoded by duplicate slo1 genes in teleost fishes.Mol Biol Evol. 2009 Jul;26(7):1509-21. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp060. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Mol Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 19321796 Free PMC article.
-
BK Channels in the Vertebrate Inner Ear.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;128:369-99. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.03.016. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27238269 Review.
-
Mechanisms of hair cell tuning.Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:809-34. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.61.1.809. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10099711 Review.
Cited by
-
Hearing conspecific vocal signals alters peripheral auditory sensitivity.Proc Biol Sci. 2015 Jun 7;282(1808):20150749. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.0749. Proc Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25972471 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic and developmental analyses indicate complex functions of calcium-activated potassium channels in zebrafish embryonic development.Dev Dyn. 2021 Oct;250(10):1477-1493. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.329. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Dev Dyn. 2021. PMID: 33728688 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroendocrine control of seasonal plasticity in the auditory and vocal systems of fish.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2015 Apr;37:129-45. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.08.002. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25168757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hearing Assessment in Zebrafish During the First Week Postfertilization.Zebrafish. 2016 Apr;13(2):79-86. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2015.1166. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Zebrafish. 2016. PMID: 26982161 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression underlying enhanced, steroid-dependent auditory sensitivity of hair cell epithelium in a vocal fish.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 14;16:782. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1940-3. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26466782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beisel K. W., Rocha-Sanchez S. M., Ziegenbein S. J., Morris K. A., Kai C., Kawai J., Carninci P., Hayashizaki Y., Davis R. L. (2007). Diversity of Ca2+-activated K+ channel transcripts in inner ear hair cells. Gene 386, 11-23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

