Modulation of endothelial glycocalyx structure under inflammatory conditions
- PMID: 24803742
- PMCID: PMC3997148
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/694312
Modulation of endothelial glycocalyx structure under inflammatory conditions
Abstract
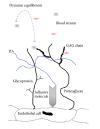
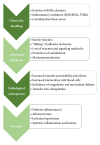
The glycocalyx of the endothelium is an intravascular compartment that creates a barrier between circulating blood and the vessel wall. The glycocalyx is suggested to play an important role in numerous physiological processes including the regulation of vascular permeability, the prevention of the margination of blood cells to the vessel wall, and the transmission of shear stress. Various theoretical models and experimental approaches provide data about changes to the structure and functions of the glycocalyx under various types of inflammatory conditions. These alterations are suggested to promote inflammatory processes in vessels and contribute to the pathogenesis of number of diseases. In this review we summarize current knowledge about the modulation of the glycocalyx under inflammatory conditions and the consequences for the course of inflammation in vessels. The structure and functions of endothelial glycocalyx are briefly discussed in the context of methodological approaches regarding the determination of endothelial glycocalyx and the uncertainty and challenges involved in glycocalyx structure determination. In addition, the modulation of glycocalyx structure under inflammatory conditions and the possible consequences for pathogenesis of selected diseases and medical conditions (in particular, diabetes, atherosclerosis, ischemia/reperfusion, and sepsis) are summarized. Finally, therapeutic strategies to ameliorate glycocalyx dysfunction suggested by various authors are discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelial Glycocalyx Impairment in Disease: Focus on Hyaluronan Shedding.Am J Pathol. 2020 Apr;190(4):768-780. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.11.016. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Am J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32035885 Review.
-
Regulation and function of endothelial glycocalyx layer in vascular diseases.Vascul Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;100:26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28919014 Review.
-
ENDOTHELIAL GLYCOCALYX AND ATHEROSCLEROSIS: FROM MOLECULAR MECHANISMS TO THERAPEUTIC OPPORTUNITIES.Georgian Med News. 2025 Mar;(360):210-217. Georgian Med News. 2025. PMID: 40466718 Review.
-
Glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and sulodexide and the endothelium: biological roles and pharmacological effects.Int Angiol. 2014 Jun;33(3):243-54. Int Angiol. 2014. PMID: 24936533 Review.
-
Endothelial Glycocalyx Turnover in Vascular Health and Disease: Rethinking Endothelial Dysfunction.Annu Rev Biochem. 2025 Jun;94(1):561-586. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-032620-104745. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Annu Rev Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40132227 Review.
Cited by
-
Choices in fluid type and volume during resuscitation: impact on patient outcomes.Ann Intensive Care. 2014 Dec 4;4:38. doi: 10.1186/s13613-014-0038-4. eCollection 2014. Ann Intensive Care. 2014. PMID: 25625012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide to repair cardiovascular injury after trauma.Nitric Oxide. 2022 Dec 1;129:82-101. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Nitric Oxide. 2022. PMID: 36280191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Endothelial Glycocalyx: A Fundamental Determinant of Vascular Permeability in Sepsis.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020 May;21(5):e291-e300. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002266. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32132499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CD44-HA axis and inflammation in atherosclerosis: A temporal perspective.Matrix Biol. 2019 May;78-79:201-218. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 May 21. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 29792915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Signaling in Allogenic Solid Organ Transplantation - The Role of Endothelial Cells.Front Physiol. 2020 May 8;11:443. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00443. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32457653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gouverneur M, van den Berg B, Nieuwdorp M, Stroes E, Vink H. Vasculoprotective properties of the endothelial glycocalyx: effects of fluid shear stress. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2006;259(4):393–400. - PubMed
-
- Tarbell JM, Weinbaum S, Kamm RD. Cellular fluid mechanics and mechanotransduction. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 2005;33(12):1719–1723. - PubMed
-
- VanTeeffelen JW, Brands J, Stroes ES, Vink H. Endothelial glycocalyx: sweet shield of blood vessels. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2007;17(3):101–105. - PubMed
-
- Becker BF, Chappell D, Bruegger D, Annecke T, Jacob M. Therapeutic strategies targeting the endothelial glycocalyx: acute deficits, but great potential. Cardiovascular Research. 2010;87(2):300–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

