Low dose intrathecal clonidine and fentanyl added to hyperbaric bupivacaine prolongs analgesia in gynecological surgery
- PMID: 24803764
- PMCID: PMC4009646
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-9185.130029
Low dose intrathecal clonidine and fentanyl added to hyperbaric bupivacaine prolongs analgesia in gynecological surgery
Abstract
Background: We undertook this study to ascertain if a small dose of clonidine (30 μg) when added to a bupivacaine-fentanyl mixture improves spinal analgesia, without producing side effects, as compared to a bupivacaine-fentanyl or a bupivacaine-clonidine mixture.
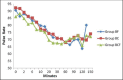
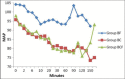
Materials and methods: In this prospective, randomized, double-blind study, 75 (American Society of Anesthesiologists) ASA grade I-II patients, aged between 45 and 65 years, who were scheduled for vaginal hysterectomy with pelvic floor repair or non-descent vaginal hysterectomy under spinal anesthesia were recruited. The patients received hyperbaric bupivacaine (2.3 ml) with fentanyl 15 μg (Group BF) or clonidine 30 μg (Group BC) or both fentanyl (15 μg) and clonidine (30 μg) (Group BCF). The total amount of intrathecal mixture was constant (2.8 ml) in all the groups. Duration of sensory, motor block and effective analgesia, hemodynamic profile, postoperative pain score and analgesic requirements were recorded.
Results: The duration of effective analgesia, mean time till two-segment regression, and duration of sensory and motor block were significantly longer in group BCF as compared to group BC (P ~ 0.002), and in group BC as compared to group BF (P ~ 0.01). The incidence of intraoperative pain and requirement of postoperative analgesics in the first 24 hours was significantly more in group BF as compared to the other groups (P ~ 0.01). There was no difference in the hemodynamic profile between the groups.
Conclusion: Low-dose clonidine (30 μg) when added to a bupivacaine-fentanyl mixture increased the duration of effective analgesia and the duration of sensory and motor block in gynecological surgery. The incidence of intraoperative pain and requirement of postoperative analgesics was significantly less when clonidine was added to intrathecal bupivacaine with or without fentanyl.
Keywords: Anesthetic; analgesia; bupivacaine; clonidine; fentanyl; postoperative; spinal.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of clonidine and/or fentanyl in combination with intrathecal bupivacaine for lower limb surgery.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Oct-Dec;31(4):485-90. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.169069. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26702205 Free PMC article.
-
Addition of intrathecal fentanyl to bupivacaine clonidine mixture effect on quality of subarachnoid block and postoperative analgesia.Anesth Essays Res. 2013 Jan-Apr;7(1):76-82. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.114003. Anesth Essays Res. 2013. PMID: 25885725 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intrathecal clonidine and fentanyl in hyperbaric bupivacaine for spinal anesthesia and postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing lower abdominal surgeries.Saudi J Anaesth. 2017 Jan-Mar;11(1):37-40. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.197337. Saudi J Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 28217051 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of the effect of clonidine, fentanyl, and the combination of both as adjuvant to intrathecal bupivacaine for postoperative analgesia in total abdominal hysterectomy.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan-Mar;33(1):102-106. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.202194. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28413281 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Intrathecal Fentanyl for Cesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials With Trial Sequential Analysis.Anesth Analg. 2020 Jan;130(1):111-125. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003975. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 30633056
Cited by
-
Effect of intrathecal clonidine versus fentanyl on bupivacaine spinal block in transurethral resection of prostate surgeries.Anesth Essays Res. 2016 Jan-Apr;10(1):65-70. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.165513. Anesth Essays Res. 2016. PMID: 26957693 Free PMC article.
-
Biased, Bitopic, Opioid-Adrenergic Tethered Compounds May Improve Specificity, Lower Dosage and Enhance Agonist or Antagonist Function with Reduced Risk of Tolerance and Addiction.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Feb 10;15(2):214. doi: 10.3390/ph15020214. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Ropivacaine and Fentanyl Versus Ropivacaine and Fentanyl with Clonidine for Postoperative Epidural Analgesia in Total Knee Replacement Surgery.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Sep;11(9):UC09-UC12. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/25401.10615. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 29207811 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Intrathecal Nalbuphine Hydrochloride and Clonidine Hydrochloride as an Adjuvant to Hyperbaric Bupivacaine in Abdominal Hysterectomy.Anesth Essays Res. 2018 Apr-Jun;12(2):402-406. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_5_18. Anesth Essays Res. 2018. PMID: 29962606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kizilarslan S, Kuvaki B, Onat U, Sağiroğlu E. Epidural fentanyl-bupivacaine compared with clonidine-bupivacaine for analgesia in labour. Eur J Anesthesiol. 2000;17:692–7. - PubMed
-
- Chiari A, Lorber C, Eisenach JC, Wildling E, Krenn C, Zavrsky A, et al. Analgesic and hemodynamic effects of intrathecal clonidine as the sole analgesic agent during first stage of labor: A dose-response study. Anesthesiology. 1999;91:388–96. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou D, Thorin D, Brichant JF, Dailland P, Milon D, Schneider M. Intrathecal clonidine and fentanyl with hyperbaric bupivacaine improves analgesia during cesarean section. Anesth Analg. 1998;87:609–13. - PubMed
-
- Heo GJ, Kim YH, Oh JH, Joo JC. Effect of intrathecal clonidine in hyperbaric bupivacaine spinal anesthesia. Korean J Anesthesiol. 1997;33:304–8.
-
- Dobrydnjov I, Axelsson K, Thörn SE, Matthiesen P, Klockhoff H, Holmström B, et al. Clonidine combined with small-dose bupivacaine during spinal anesthesia for inguinal herniorrhaphy: A randomized double-blinded study. Anesth Analg. 2003;96:1496–503. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

