Serum amyloid P: a systemic regulator of the innate immune response
- PMID: 24804675
- PMCID: PMC6607997
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1MR0114-068R
Serum amyloid P: a systemic regulator of the innate immune response
Abstract
The pentraxin SAP reduces neutrophil adhesion to ECM proteins, inhibits the differentiation of monocytes into fibrocytes, attenuates profibrotic macrophages, activates the complement pathway, and promotes phagocytosis of cell debris. Together, these effects of SAP regulate key aspects of inflammation and set a threshold for immune cell activation. Here, we present a review of SAP biology with an emphasis on SAP receptor interactions and how the effect of SAP on monocytes and macrophages has been explored to develop this protein as a therapeutic for renal and lung injuries. We also discuss how there remain many unanswered questions about the role of SAP in innate immunity.
Keywords: Fcγ receptors; fibrocyte differentiation; fibrosis; macrophage polarization; neutrophil adhesion; phagocytosis.
© 2014 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Figures
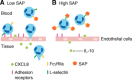
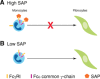
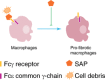
References
-
- Janeway C. A., Jr. , Medzhitov, R. (2002) Innate immune recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 197–216. - PubMed
-
- Boehm, T. (2012) Evolution of vertebrate immunity. Curr. Biol. 22, R722–R732. - PubMed
-
- Mantovani, A. S. , Biswas, M. Galdiero R., Sica, A. , Locati, M. (2013) Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J. Pathol. 229, 176–185. - PubMed
-
- Deban, L. , Jaillon, S. , Garlanda, C. , Bottazzi, B. , Mantovani, A. (2011) Pentraxins in innate immunity: lessons from PTX3. Cell Tissue Res. 343, 237–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

