Self-gated fat-suppressed cardiac cine MRI
- PMID: 24806049
- PMCID: PMC4224643
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25291
Self-gated fat-suppressed cardiac cine MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a self-gated alternating repetition time balanced steady-state free precession (ATR-SSFP) pulse sequence for fat-suppressed cardiac cine imaging.
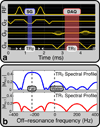
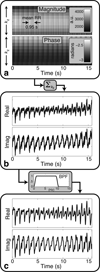
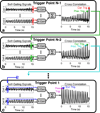
Methods: Cardiac gating is computed retrospectively using acquired magnetic resonance self-gating data, enabling cine imaging without the need for electrocardiogram (ECG) gating. Modification of the slice-select rephasing gradients of an ATR-SSFP sequence enables the acquisition of a one-dimensional self-gating readout during the unused short repetition time (TR). Self-gating readouts are acquired during every TR of segmented, breath-held cardiac scans. A template-matching algorithm is designed to compute cardiac trigger points from the self-gating signals, and these trigger points are used for retrospective cine reconstruction. The proposed approach is compared with ECG-gated ATR-SSFP and balanced steady-state free precession in 10 volunteers and five patients.
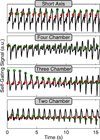
Results: The difference of ECG and self-gating trigger times has a variability of 13 ± 11 ms (mean ± SD). Qualitative reviewer scoring and ranking indicate no statistically significant differences (P > 0.05) between self-gated and ECG-gated ATR-SSFP images. Quantitative blood-myocardial border sharpness is not significantly different among self-gated ATR-SSFP ( 0.61±0.15 mm -1), ECG-gated ATR-SSFP ( 0.61±0.15 mm -1), or conventional ECG-gated balanced steady-state free precession cine MRI ( 0.59±0.15 mm -1).
Conclusion: The proposed self-gated ATR-SSFP sequence enables fat-suppressed cardiac cine imaging at 1.5 T without the need for ECG gating and without decreasing the imaging efficiency of ATR-SSFP.
Keywords: alternating repetition time; cardiac imaging; cine magnetic resonance imaging; self gating; steady-state free precession.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

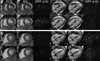
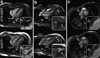
References
-
- Manning WJ, Pennell DJ. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier; 2010.
-
- Polson MJ, Barker AT, Gardiner S. The effect of rapid rise-time magnetic fields on the ECG of the rat. Clin Phys Physiol Meas. 1982;3:231–234. - PubMed
-
- Shetty AN. Suppression of radiofrequency interference in cardiac gated MRI: a simple design. Magn Reson Med. 1988;8:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Becker M, Frauenrath T, Hezel F, Krombach GA, Kremer U, Koppers B, Butenweg C, Goemmel A, Utting JF, Schulz-Menger J, Niendorf T. Comparison of left ventricular function assessment using phonocardiogram- and electrocardiogram-triggered 2D SSFP CINE MR imaging at 1.5 T and 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:1344–1355. - PubMed
-
- Spraggins TA. Wireless retrospective gating: application to cine cardiac imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1990;8:675–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

