Nanopore biosensor for label-free and real-time detection of anthrax lethal factor
- PMID: 24806593
- PMCID: PMC4039345
- DOI: 10.1021/am500749p
Nanopore biosensor for label-free and real-time detection of anthrax lethal factor
Abstract
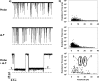
We report a label-free real-time nanopore sensing method for the detection of anthrax lethal factor, a component of the anthrax toxin, by using a complementary single-stranded DNA as a molecular probe. The method is rapid and sensitive: sub-nanomolar concentrations of the target anthrax lethal factor DNA could be detected in ∼1 min. Further, our method is selective, which can differentiate the target DNA from other single-stranded DNA molecules at the single-base resolution. This sequence-specific detection approach should find useful application in the development of nanopore sensors for the detection of other pathogens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of anthrax lef with DNA-based photonic crystal sensors.J Biomed Opt. 2011 Dec;16(12):127006. doi: 10.1117/1.3662460. J Biomed Opt. 2011. PMID: 22191936
-
Nanopore-Assisted, Sequence-Specific Detection, and Single-Molecule Hybridization Analysis of Short, Single-Stranded DNAs.Anal Chem. 2019 Jul 2;91(13):8630-8637. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02080. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31194518
-
Sequence-specific detection of single-stranded DNA with a gold nanoparticle-protein nanopore approach.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 9;10(1):11323. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68258-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647249 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Anthrax Detection: Overview of Bioprobes and Biosensors.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;176(4):957-77. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1625-z. Epub 2015 May 19. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25987133 Review.
-
[The molecular nature of Bacillus anthracis toxin].Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1991 Jan;(1):3-10. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1991. PMID: 1902551 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Potential Deployment of Biosensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Developing Countries: Technological, Economic and Regulatory Aspects.Biosensors (Basel). 2018 Nov 29;8(4):119. doi: 10.3390/bios8040119. Biosensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30501052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanopore-based detection of periodontitis biomarker miR31 in saliva samples.Electrophoresis. 2024 Nov;45(21-22):2034-2044. doi: 10.1002/elps.202400134. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Electrophoresis. 2024. PMID: 39165194
-
Sensing Microorganisms Using Rapid Detection Methods: Supramolecular Approaches.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;15(3):130. doi: 10.3390/bios15030130. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Label-Free Detection of DNA Mutations by Nanopore Analysis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 Apr 11;10(14):11519-11528. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b19774. Epub 2018 Mar 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 29537824 Free PMC article.
-
A highly sensitive nanopore platform for measuring RNase A activity.Talanta. 2024 Aug 15;276:126276. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126276. Epub 2024 May 22. Talanta. 2024. PMID: 38796995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update; World Health Organization: Genève, 2008.
-
- Foudeh A. M.; Fatanat Didar T.; Veres T.; Tabrizian M. Microfluidic Designs and Techniques Using Lab-on-a-Chip Devices for Pathogen Detection for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3249–3266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

