Bladder afferent hyperexcitability in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
- PMID: 24807488
- PMCID: PMC4089034
- DOI: 10.1111/iju.12308
Bladder afferent hyperexcitability in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
Abstract
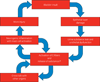
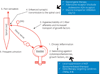
Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis is a disease with lower urinary tract symptoms, such as bladder pain and urinary frequency, which results in seriously impaired quality of life of patients. The extreme pain and urinary frequency are often difficult to treat. Although the etiology of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis is still not known, there is increasing evidence showing that afferent hyperexcitability as a result of neurogenic bladder inflammation and urothelial dysfunction is important to the pathophysiological basis of symptom development. Further investigation of the pathophysiology will lead to the effective treatment of patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis.
Keywords: afferent pathway; bladder pain syndrome; cytokine; interstitial cystitis; nerve growth factor.
© 2014 The Japanese Urological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Chancellor MB, Yoshimura N. Treatment of interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2004;63(3 Suppl 1):85–92. - PubMed
-
- Homma Y, Ueda T, Ito T, Takei M, Tomoe H. Japanese guideline for diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis. Int. J. Urol. 2009;16:4–16. - PubMed
-
- Parsons CL, Benson G, Childs SJ, Hanno P, Sant GR, Webster G. A quantitatively controlled method to study prospectively interstitial cystitis and demonstrate the efficacy of pentosanpolysulfate. J. Urol. 1993;150:845–848. - PubMed
-
- Hanno PM, Landis JR, Matthews-Cook Y, Kusek J, Nyberg L., Jr The diagnosis of interstitial cystitis revisited: lessons learned from the National Institutes of Health Interstitial Cystitis Database study. J. Urol. 1999;161:553–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

