Two-position supine/prone myocardial perfusion SPECT (MPS) imaging improves visual inter-observer correlation and agreement
- PMID: 24807622
- PMCID: PMC4158826
- DOI: 10.1007/s12350-014-9895-3
Two-position supine/prone myocardial perfusion SPECT (MPS) imaging improves visual inter-observer correlation and agreement
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to compare the inter-observer agreement between two experienced readers using supine vs combined supine/prone myocardial perfusion SPECT (MPS) in a large population.
Methods: 1,181 consecutive patients without known coronary artery disease (CAD) undergoing rest (201)Tl/stress (99m)Tc-sestamibi MPS studies were evaluated. Visual reads were performed in two consecutive steps, with readers scoring the stress supine perfusion images during step 1 and rescoring the images using both supine/prone data during step 2. Visual summed stress scores (SSS) of two readers including regional scores in different vascular territories were compared.
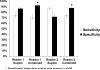
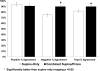
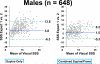
Results: The specificity for both readers improved using combined supine/prone imaging (reader 1: 92% vs 86% [P = .0002], reader 2: 88% vs 72% [P < .0001]). The inter-observer correlation for SSS (0.90 vs 0.84, P < .0001) and inter-observer agreement for combined supine/prone reading (bias = 1.0, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.9-1.2 vs bias = 3.1, 95% CI 2.8-3.4, P < .0001) were significantly better as compared to supine-only reading. The overall correlation between SSS scores for two readers improved with supine/prone imaging for both genders, as well as in the left anterior descending and right coronary territories.
Conclusion: The inter-observer correlation and agreement significantly improve using two-position supine/prone vs supine-only imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Danias PG, Ahlberg AW, Travin MI, Mahr NC, Abreu JE, Marini D, et al. Visual assessment of left ventricular perfusion and function with electrocardiography-gated SPECT has high intraobserver and interobserver reproducibility among experienced nuclear cardiologists and cardiology trainees. J Nucl Cardiol. 2002;9:263–270. - PubMed
-
- Berman DS, Kang X, Nishina H, Slomka PJ, Shaw LJ, Hayes SW, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of gated Tc-99m sestamibi stress myocardial perfusion SPECT with combined supine and prone acquisitions to detect coronary artery disease in obese and nonobese patients. J Nucl Cardiol. 2006;13:191–201. - PubMed
-
- Slomka PJ, Nishina H, Abidov A, Hayes SW, Friedman JD, Berman DS, et al. Combined quantitative supine-prone myocardial perfusion SPECT improves detection of coronary artery disease and normalcy rates in women. J Nucl Cardiol. 2007;14:44–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

