IL-21 receptor signalling partially mediates Th2-mediated allergic airway responses
- PMID: 24807637
- PMCID: PMC4083497
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.12341
IL-21 receptor signalling partially mediates Th2-mediated allergic airway responses
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-21 (IL-21) has been implicated in the development of Th2-mediated immune responses; however, the exact role it plays in allergic diseases is not well understood.
Objective: To elucidate the contribution of IL-21 receptor signalling to Th2-dependent immune responses in the lung.
Methods: We compared allergic airway responses in wild-type BALB/c and Il21r-deficient mice exposed to local airway challenge with house dust mite (HDM).
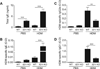
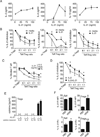
Results: We demonstrate that IL-21R-deficiency reduces HDM-driven airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) with only partial effects on airway inflammation. Concomitant with the reduction in AHR in Il21r-deficient mice, significant suppression was observed in protein levels of the Th2 cytokines IL-4, and IL-13. In contrast, IL-21R-deficiency was associated with an increase in PBS- and allergen-driven IgE levels, while IgG1 and IgG2a levels were decreased. Moreover, our results suggest that IL-21 may contribute to AHR through its ability to both directly induce Th2 cell survival and to impair regulatory T-cell suppression of Th2 cytokine production. Importantly, we show that IL-21-positive cells are increased in the bronchial mucosa of asthmatics compared with non-asthmatics.
Conclusion: These results suggest that IL-21 plays an important role in the allergic diathesis by enhancing Th2 cytokine production through multiple mechanisms including the suppression of Treg inhibitory effects on Th2 cell cytokine production.
Keywords: IL-21; IL-21R; Tregs; airway hyperresponsiveness; asthma.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Frohlich A, Marsland BJ, Sonderegger I, Kurrer M, Hodge MR, Harris NL, et al. IL-21 receptor signaling is integral to the development of Th2 effector responses in vivo. Blood. 2007;109(5):2023–2031. Epub 2006/11/02. - PubMed
-
- Nurieva R, Yang XO, Martinez G, Zhang Y, Panopoulos AD, Ma L, et al. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21 in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature. 2007;448(7152):480–483. Epub 2007/06/22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

