Novel (ovario) leukodystrophy related to AARS2 mutations
- PMID: 24808023
- PMCID: PMC4118500
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000497
Novel (ovario) leukodystrophy related to AARS2 mutations
Abstract
Objectives: The study was focused on leukoencephalopathies of unknown cause in order to define a novel, homogeneous phenotype suggestive of a common genetic defect, based on clinical and MRI findings, and to identify the causal genetic defect shared by patients with this phenotype.
Methods: Independent next-generation exome-sequencing studies were performed in 2 unrelated patients with a leukoencephalopathy. MRI findings in these patients were compared with available MRIs in a database of unclassified leukoencephalopathies; 11 patients with similar MRI abnormalities were selected. Clinical and MRI findings were investigated.
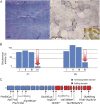
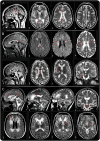
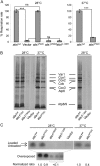
Results: Next-generation sequencing revealed compound heterozygous mutations in AARS2 encoding mitochondrial alanyl-tRNA synthetase in both patients. Functional studies in yeast confirmed the pathogenicity of the mutations in one patient. Sanger sequencing revealed AARS2 mutations in 4 of the 11 selected patients. The 6 patients with AARS2 mutations had childhood- to adulthood-onset signs of neurologic deterioration consisting of ataxia, spasticity, and cognitive decline with features of frontal lobe dysfunction. MRIs showed a leukoencephalopathy with striking involvement of left-right connections, descending tracts, and cerebellar atrophy. All female patients had ovarian failure. None of the patients had signs of a cardiomyopathy.
Conclusions: Mutations in AARS2 have been found in a severe form of infantile cardiomyopathy in 2 families. We present 6 patients with a new phenotype caused by AARS2 mutations, characterized by leukoencephalopathy and, in female patients, ovarian failure, indicating that the phenotypic spectrum associated with AARS2 variants is much wider than previously reported.
© 2014 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Rötig A. Human diseases with impaired mitochondrial protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011;1807:1198–1205 - PubMed
-
- Konovalova S, Tyynismaa T. Mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in human disease. Mol Genet Metab 2013;108:206–211 - PubMed
-
- Scheper GC, van der Klok T, van Andel RJ, et al. Mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA synthetase deficiency causes leukoencephalopathy with brain stem and spinal cord involvement and lactate elevation. Nat Genet 2007;39:534–539 - PubMed
-
- Steenweg ME, Ghezzi D, Haack T, et al. Leukoencephalopathy with thalamus and brainstem involvement and high lactate “LTBL” caused by EARS2 mutations. Brain 2012;135:1387–1394 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
