First D1-like receptor PET imaging of the rat and primate kidney: implications for human disease monitoring
- PMID: 24808534
- PMCID: PMC4347741
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00111.2014
First D1-like receptor PET imaging of the rat and primate kidney: implications for human disease monitoring
Abstract
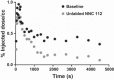
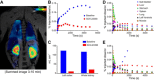
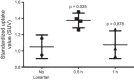
The intrarenal dopamine system is important for signaling and natriuresis, and significant dysfunction is associated with hypertension and kidney disease in ex vivo studies. Dopamine receptors also modulate and are modulated by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Here, we show the first in vivo measurement of D1-like receptors in the renal cortex of Sprague-Dawley rat and Papio anubis baboon using [(11)C]NNC 112, a positron emission tomography radioligand for D1-like receptors. In addition, we show a D1-like binding potential response to angiotensin II blockade in rats using losartan. Demonstration of self-saturable binding in the rat as well as specific and saturable binding in Papio anubis validate the use of [(11)C]NNC 112 in the first in vivo measurement of renal dopamine D1-like receptors. Furthermore, [(11)C]NNC 112 is a radioligand tool already validated for use in probing human central nervous system (CNS) D1-like receptors. Our work demonstrates specific and saturable non-CNS binding in higher animals and the ability to quantify physiological response to drug treatment and provides a clear path to extend use of [(11)C]NNC 112 to study renal dopamine in humans.
Keywords: dopamine; hypertension; positron emission tomography; renal PET; renal dopamine.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
11C- and 76Br-labelled NNC 22-0010, selective dopamine D1 receptor radioligands for PET.Nucl Med Biol. 1996 Aug;23(6):837-44. doi: 10.1016/0969-8051(96)00083-2. Nucl Med Biol. 1996. PMID: 8940728
-
PET studies of binding competition between endogenous dopamine and the D1 radiotracer [11C]NNC 756.Synapse. 1999 May;32(2):93-109. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199905)32:2<93::AID-SYN3>3.0.CO;2-C. Synapse. 1999. PMID: 10231129
-
Dopamine depletion and in vivo binding of PET D1 receptor radioligands: implications for imaging studies in schizophrenia.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003 Sep;28(9):1703-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300224. Epub 2003 Jun 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12813475
-
Clozapine: dopamine D1 receptor agonism in the prefrontal cortex as the code to decipher a Rosetta stone of antipsychotic drugs.Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999 May;84(5):193-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1999.tb01482.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999. PMID: 10361974 Review.
-
Dopamine receptor interacting proteins (DRIPs) of dopamine D1-like receptors in the central nervous system.Mol Cells. 2008 Apr 30;25(2):149-57. Epub 2008 Mar 28. Mol Cells. 2008. PMID: 18414018 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine D1R Receptor Stimulation as a Mechanistic Pro-cognitive Target for Schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2022 Jan 21;48(1):199-210. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbab095. Schizophr Bull. 2022. PMID: 34423843 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammatory component of gray matter pathology in multiple sclerosis.Ann Neurol. 2016 Nov;80(5):776-790. doi: 10.1002/ana.24791. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Ann Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27686563 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of cortico-meningeal translocator protein expression in multiple sclerosis.Brain. 2024 Jul 5;147(7):2566-2578. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae030. Brain. 2024. PMID: 38289855 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive mechanisms of intra-renal dopamine.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015 Mar;24(2):117-22. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000104. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25594544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrams AC. Clinical Drug Therapy: Rationales for Nursing Practice (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007.
-
- Aperia AC. Intrarenal dopamine: a key signal in the interactive regulation of sodium metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 62: 621–647, 2000. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

