pH-responsive, gluconeogenic renal epithelial LLC-PK1-FBPase+cells: a versatile in vitro model to study renal proximal tubule metabolism and function
- PMID: 24808535
- PMCID: PMC4080158
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00067.2014
pH-responsive, gluconeogenic renal epithelial LLC-PK1-FBPase+cells: a versatile in vitro model to study renal proximal tubule metabolism and function
Abstract
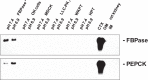
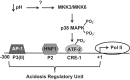
Ammoniagenesis and gluconeogenesis are prominent metabolic features of the renal proximal convoluted tubule that contribute to maintenance of systemic acid-base homeostasis. Molecular analysis of the mechanisms that mediate the coordinate regulation of the two pathways required development of a cell line that recapitulates these features in vitro. By adapting porcine renal epithelial LLC-PK1 cells to essentially glucose-free medium, a gluconeogenic subline, termed LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells, was isolated. LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells grow in the absence of hexoses and pentoses and exhibit enhanced oxidative metabolism and increased levels of phosphate-dependent glutaminase. The cells also express significant levels of the key gluconeogenic enzymes, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK). Thus the altered phenotype of LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells is pleiotropic. Most importantly, when transferred to medium that mimics a pronounced metabolic acidosis (9 mM HCO3 (-), pH 6.9), the LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells exhibit a gradual increase in NH4 (+) ion production, accompanied by increases in glutaminase and cytosolic PEPCK mRNA levels and proteins. Therefore, the LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells retained in culture many of the metabolic pathways and pH-responsive adaptations characteristic of renal proximal tubules. The molecular mechanisms that mediate enhanced expression of the glutaminase and PEPCK in LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells have been extensively reviewed. The present review describes novel properties of this unique cell line and summarizes the molecular mechanisms that have been defined more recently using LLC-PK1-FBPase(+) cells to model the renal proximal tubule. It also identifies future studies that could be performed using these cells.
Keywords: acid-base balance; ammoniagenesis; gluconeogenesis; pH-responsive; proximal tubule.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Brosnan JT, Lowry M, Vinay P, Gougoux A, Halperin ML. Renal ammonia production—une vue canadienne. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 65: 489–498, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Burch HB, Narins RG, Chu C, Fagioli S, Choi S, McCarthy W, Lowry OH. Distribution along the rat nephron of three enzymes of gluconeogenesis in acidosis and starvation. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 235: F246–F253, 1978 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

