Respiratory electron transfer pathways in plant mitochondria
- PMID: 24808901
- PMCID: PMC4010797
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00163
Respiratory electron transfer pathways in plant mitochondria
Abstract
The respiratory electron transport chain (ETC) couples electron transfer from organic substrates onto molecular oxygen with proton translocation across the inner mitochondrial membrane. The resulting proton gradient is used by the ATP synthase complex for ATP formation. In plants, the ETC is especially intricate. Besides the "classical" oxidoreductase complexes (complex I-IV) and the mobile electron transporters cytochrome c and ubiquinone, it comprises numerous "alternative oxidoreductases." Furthermore, several dehydrogenases localized in the mitochondrial matrix and the mitochondrial intermembrane space directly or indirectly provide electrons for the ETC. Entry of electrons into the system occurs via numerous pathways which are dynamically regulated in response to the metabolic state of a plant cell as well as environmental factors. This mini review aims to summarize recent findings on respiratory electron transfer pathways in plants and on the involved components and supramolecular assemblies.
Keywords: alternative oxidase; dehydrogenase; electron transport chain; plant mitochondria; respiratory supercomplex.
Figures
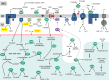

References
-
- Araújo W. L., Ishizaki K., Nunes-Nesi A., Larson T. R., Tohge T., Krahnert I., et al. (2010). Identification of the 2-hydroxyglutarate and isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenases as alternative electron donors linking lysine catabolism to the electron transport chain of Arabidopsis mitochondria. Plant Cell 22, 1549–1563 10.1105/tpc.110.075630 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araújo W. L., Nunes-Nesi A., Trenkamp S., Bunik V. I., Fernie A. R. (2008). Inhibition of 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase in potato tuber suggests the enzyme is limiting for respiration and confirms its importance in nitrogen assimilation. Plant Physiol. 148, 1782–1796 10.1104/pp.108.126219 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

