Genomic and proteomic characterization of bacteriocin-producing Leuconostoc mesenteroides strains isolated from raw camel milk in two southwest Algerian arid zones
- PMID: 24809059
- PMCID: PMC3997938
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/853238
Genomic and proteomic characterization of bacteriocin-producing Leuconostoc mesenteroides strains isolated from raw camel milk in two southwest Algerian arid zones
Abstract
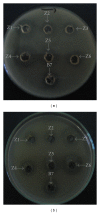
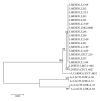
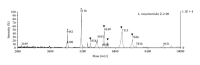
Information on the microbiology of camel milk is very limited. In this work, the genetic characterization and proteomic identification of 13 putative producing bacteriocin Leuconostoc strains exhibiting antilisterial activity and isolated from camel milk were performed. DNA sequencing of the 13 selected strains revealed high homology among the 16S rRNA genes for all strains. In addition, 99% homology with Leuconostoc mesenteroides was observed when these sequences were analysed by the BLAST tool against other sequences from reference strains deposited in the Genbank. Furthermore, the isolates were characterized by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDITOF MS) which allowed for the identification of 2 mass peaks 6242 m/z and 5118 m/z that resulted to be specific to the species L. mesenteroides. Remarkably, the phyloproteomic tree provided more intraspecific information of L. mesenteroides than phylogenetic analysis. Accordingly, phyloproteomic analysis grouped L. mesenteroides strains into different subbranches, while all L. mesenteroides isolates were grouped in the same branch according to phylogenetic analysis. This study represents, to our knowledge, the first report on the use of MALDI-TOF MS on the identification of LAB isolated from camel milk.
Figures


Similar articles
-
16S rRNA gene sequencing and MALDI TOF mass spectroscopy identification of Leuconostoc mesenteroides isolated from Algerian raw camel milk.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023 May 1;21(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00500-1. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37126186 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenterocin 52, a bacteriocin produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides ssp. mesenteroides FR 52.J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;74(4):372-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb05141.x. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8486542
-
Technological aptitude and applications of Leuconostoc mesenteroides bioactive strains isolated from Algerian raw camel milk.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:418132. doi: 10.1155/2013/418132. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24392451 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriocins of leuconostocs isolated from meat.Int J Food Microbiol. 1994 Dec;24(1-2):75-81. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(94)90107-4. Int J Food Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 7703031 Review.
-
Bacteriocins produced by Leuconostoc species.J Dairy Sci. 1994 Sep;77(9):2718-24. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(94)77214-3. J Dairy Sci. 1994. PMID: 7814741 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotransmitter metabolites in milk ferments of Leuconostoc mesenteroides regulate temperature-sensitive heartbeats in an ex ovo model.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 11;10(16):e36129. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36129. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39253113 Free PMC article.
-
16S rRNA gene sequencing and MALDI TOF mass spectroscopy identification of Leuconostoc mesenteroides isolated from Algerian raw camel milk.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023 May 1;21(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s43141-023-00500-1. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37126186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piard JC, Desmazeaud M. Inhibiting factors produced by lactic acid bacteria. 2. Bacteriocins and other antibacterial substances. Lait. 1992;72(2):113–142.
-
- Felix JV, Papathanasopoulos MA, Smith AA, Von Holy A, Hastings JW. Characterization of leucocin B-Ta11a: a bacteriocin from Leuconostoc carnosum Ta11a isolated from meat. Current Microbiology. 1994;29(4):207–212. - PubMed
-
- Hastings JW, Gibson PT, Chauhan R, Dykes GA, Von Holy A. Similarity of bacteriocins from spoiled meat lactic acid bacteria. South African Journal of Science. 1996;92(8):376–380.
-
- Osmanağaoğlu O. Detection and characterization of Leucocin OZ, a new anti-listerial bacteriocin produced by Leuconostoc carnosum with a broad spectrum of activity. Food Control. 2007;18(2):118–123.
-
- van Laack RLJM, Schillinger U, Holzapfel WH. Characterization and partial purification of a bacteriocin produced by Leuconostoc carnosum LA44A. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 1992;16(3):183–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

