Linear superposition and prediction of bacterial promoter activity dynamics in complex conditions
- PMID: 24809350
- PMCID: PMC4014397
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003602
Linear superposition and prediction of bacterial promoter activity dynamics in complex conditions
Abstract
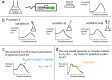
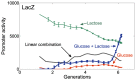
Bacteria often face complex environments. We asked how gene expression in complex conditions relates to expression in simpler conditions. To address this, we obtained accurate promoter activity dynamical measurements on 94 genes in E. coli in environments made up of all possible combinations of four nutrients and stresses. We find that the dynamics across conditions is well described by two principal component curves specific to each promoter. As a result, the promoter activity dynamics in a combination of conditions is a weighted average of the dynamics in each condition alone. The weights tend to sum up to approximately one. This weighted-average property, called linear superposition, allows predicting the promoter activity dynamics in a combination of conditions based on measurements of pairs of conditions. If these findings apply more generally, they can vastly reduce the number of experiments needed to understand how E. coli responds to the combinatorially huge space of possible environments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Hengge R, Storz G, American Society for Microbiology (2011) Bacterial stress responses.
-
- Hoch JA, Silhavy TJ (1995) Two-component signal transduction. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press.
-
- Neidhardt FC (1996) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology.
-
- Ptashne M, Gann A (2002) Genes and Signals. CSHL Press. 214 p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

