The role of inflammation for a successful implantation
- PMID: 24809430
- PMCID: PMC6800188
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.12266
The role of inflammation for a successful implantation
Abstract
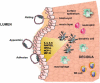
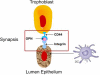
Approximately half of all human embryo implantations result in failed pregnancy. Multiple factors may contribute to this failure, including genetic or metabolic abnormalities of the embryo. However, many of these spontaneous early abortion cases are attributed to poor uterine receptivity. Furthermore, although many fertility disorders have been overcome by a variety of assisted reproductive techniques, implantation remains the rate-limiting step for the success of the in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments. We, as well as others, have demonstrated that endometrial biopsies performed either during the spontaneous, preceding cycle, or during the IVF cycle itself, significantly improve the rate of implantation, clinical pregnancies, and live births. These observations suggest that mechanical injury of the endometrium may enhance uterine receptivity by provoking the immune system to generate an inflammatory reaction. In strong support of this idea, we recently found that dendritic cells (DCs), an important cellular component of the innate immune system, play a critical role in successful implantation in a mouse model. In this review, we discuss the hypothesis that the injury-derived inflammation in the biopsy-treated patients generates a focus for uterine DCs and Mac accumulation that, in turn, enhance the endometrial expression of essential molecules that facilitate the interaction between the embryo and the uterine epithelium.
Keywords: Dendritic cells; implantation; inflammation; pregnancy.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Wang H, Dey SK. Road map to embryo implantation: clues from mouse models. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2006;7:185–199. - PubMed
-
- Dunn CL, Kelly RW, Critchley HO. Decidualization of the human endometrial stromal cell: an enigmatic transformation. Reprod Biomed Online. 2003;7:151–161. - PubMed
-
- Paria BC, Reese J, Das SK, Dey SK. Deciphering the cross-talk of implantation: advances and challenges. Science. 2002;296:2185–2188. - PubMed
-
- van Mourik MS, Heijnen CJ, Macklon NS. Embryonic implantation: cytokines, adhesion molecules, and immune cells in establishing an implantation environment. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;85:4–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

