Interspinous spacer versus traditional decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24809680
- PMCID: PMC4014612
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097142
Interspinous spacer versus traditional decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Dynamic interspinous spacers, such as X-stop, Coflex, DIAM, and Aperius, are widely used for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. However, controversy remains as to whether dynamic interspinous spacer use is superior to traditional decompressive surgery.
Methods: Medline, Embase, Cochrane Library, and the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register were searched during August 2013. A track search was performed on February 27, 2014. Study was included in this review if it was: (1) a randomized controlled trial (RCT) or non-randomized prospective comparison study, (2) comparing the clinical outcomes for interspinous spacer use versus traditional decompressive surgery, (3) in a minimum of 30 patients, (4) with a follow-up duration of at least 12 months.
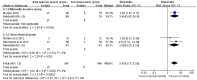
Results: Two RCTs and three non-randomized prospective studies were included, with 204 patients in the interspinous spacer (IS) group and 217 patients in the traditional decompressive surgery (TDS) group. Pooled analysis showed no significant difference between the IS and TDS groups for low back pain (WMD: 1.2; 95% CI: -10.12, 12.53; P = 0.03; I2 = 66%), leg pain (WMD: 7.12; 95% CI: -3.88, 18.12; P = 0.02; I2 = 70%), ODI (WMD: 6.88; 95% CI: -14.92, 28.68; P = 0.03; I2 = 79%), RDQ (WMD: -1.30, 95% CI: -3.07, 0.47; P = 0.00; I2 = 0%), or complications (RR: 1.39; 95% CI: 0.61, 3.14; P = 0.23; I2 = 28%). The TDS group had a significantly lower incidence of reoperation (RR: 3.34; 95% CI: 1.77, 6.31; P = 0.60; I2 = 0%).
Conclusion: Although patients may obtain some benefits from interspinous spacers implanted through a minimally invasive technique, interspinous spacer use is associated with a higher incidence of reoperation and higher cost. The indications, risks, and benefits of using an interspinous process device should be carefully considered before surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kovacs FM, Urrutia G, Alarcon JD (2011) Surgery versus conservative treatment for symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36: E1335–1351. - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui M, Smith FW, Wardlaw D (2007) One-year results of X Stop interspinous implant for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32: 1345–1348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

