The Longissimus and Semimembranosus muscles display marked differences in their gene expression profiles in pig
- PMID: 24809746
- PMCID: PMC4014511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096491
The Longissimus and Semimembranosus muscles display marked differences in their gene expression profiles in pig
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100113
Abstract
Background: Meat quality depends on skeletal muscle structure and metabolic properties. While most studies carried on pigs focus on the Longissimus muscle (LM) for fresh meat consumption, Semimembranosus (SM) is also of interest because of its importance for cooked ham production. Even if both muscles are classified as glycolytic muscles, they exhibit dissimilar myofiber composition and metabolic characteristics. The comparison of LM and SM transcriptome profiles undertaken in this study may thus clarify the biological events underlying their phenotypic differences which might influence several meat quality traits.
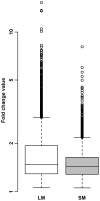
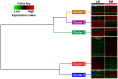
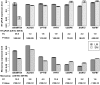
Methodology/principal findings: Muscular transcriptome analyses were performed using a custom pig muscle microarray: the 15 K Genmascqchip. A total of 3823 genes were differentially expressed between the two muscles (Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P value ≤0.05), out of which 1690 and 2133 were overrepresented in LM and SM respectively. The microarray data were validated using the expression level of seven differentially expressed genes quantified by real-time RT-PCR. A set of 1047 differentially expressed genes with a muscle fold change ratio above 1.5 was used for functional characterization. Functional annotation emphasized five main clusters associated to transcriptome muscle differences. These five clusters were related to energy metabolism, cell cycle, gene expression, anatomical structure development and signal transduction/immune response.
Conclusions/significance: This study revealed strong transcriptome differences between LM and SM. These results suggest that skeletal muscle discrepancies might arise essentially from different post-natal myogenic activities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Schwab CR, Baas TJ, Stalder KJ, Mabry JW (2006) Effect of long-term selection for increased leanness on meat and eating quality traits in Duroc swine. Journal of Animal Science 84: 1577–1583. - PubMed
-
- Rosenvold K, Andersen HJ (2003) Factors of significance for pork quality–a review. Meat Sci 64: 219–237. - PubMed
-
- Lefaucheur L (2010) A second look into fibre typing - Relation to meat quality. Meat Sci 84: 257–270. - PubMed
-
- Gentry JG, McGlone JJ, Miller MF, Blanton JR Jr (2004) Environmental effects on pig performance, meat quality, and muscle characteristics. J Anim Sci 82: 209–217. - PubMed
-
- Lefaucheur L, Lebret B, Ecolan P, Louveau I, Damon M, et al. (2010) Muscle characteristics and meat quality traits are affected by divergent selection on residual feed intake in pigs. J Anim Sci: 996–1010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

