Comparison of radiological and clinical features of temporal lobe necrosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with 2D radiotherapy or intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- PMID: 24809780
- PMCID: PMC4037838
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.243
Comparison of radiological and clinical features of temporal lobe necrosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with 2D radiotherapy or intensity-modulated radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: To compare the imaging and clinical features of temporal lobe necrosis (TLN) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients treated with two-dimensional radiotherapy (2D-RT) or those with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT).
Methods: We retrospectively analysed NPC patients who underwent 2D-RT (72 patients, 128 temporal lobes) or IMRT (36 patients, 50 lobes) and developed radiation-induced, MRI-confirmed TLN.
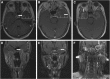
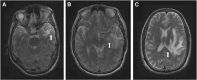
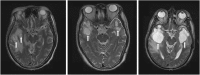
Results: White-matter lesions (WMLs), contrast-enhanced lesions, cysts and local mass effects were present in 128 out of 128 vs 48 out of 50 (P=0.078), 123 out of 128 vs 47 out of 50 (P=0.688), 10 out of 128 vs 1 out of 50 (P=0.185) and 57 out of 128 vs 13 out of 50 (P=0.023) temporal lobes, respectively, in the 2D-RT and IMRT groups. The WMLs were more extensive in the 2D-RT group (P<0.001). The maximum diameter of contrast-enhanced lesions was greater in the 2D-RT group (P<0.001), and these lesions tended to extend far away from the nasopharynx. The WMLs and enhancement had no impact on cyst development (both P=1). Local mass effects were always accompanied with contrast-enhanced lesions (P=0.024) but were not correlated with WMLs or cysts (P=0.523 and 0.341, respectively). There were no between-group differences in clinical features (all P-values>0.05), whereas the difference in the incidence of severe debility was of marginal significance (18.1% vs 5.6%, P=0.077).
Conclusions: The IMRT-induced TLN was less extensive and milder than 2D-RT-induced TLN, but both had similar clinical features.
Figures
References
-
- Butler CR, Zeman AZ. Recent insights into the impairment of memory in epilepsy: transient epileptic amnesia, accelerated long-term forgetting and remote memory impairment. Brain. 2008;131 (Pt 9:2243–2263. - PubMed
-
- Coderre JA, Morris GM, Micca PL, Hopewell JW, Verhagen I, Kleiboer BJ, van der Kogel AJ. Late effects of radiation on the central nervous system: role of vascular endothelial damage and glial stem cell survival. Radiat Res. 2006;166 (3:495–503. - PubMed
-
- Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A, American Joint Committee on Cancer 2010AJCC Cancer Staging Manual7th edn.Springer: New York
-
- Hsiao KY, Yeh SA, Chang CC, Tsai PC, Wu JM, Gau JS. Cognitive function before and after intensity-modulated radiation therapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77 (3:722–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

