SERPINB3 is associated with TGF-β1 and cytoplasmic β-catenin expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with poor prognosis
- PMID: 24809782
- PMCID: PMC4037839
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.246
SERPINB3 is associated with TGF-β1 and cytoplasmic β-catenin expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with poor prognosis
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most important sanitary problems for its prevalence and poor prognosis. To date, no information is available on the prognostic value of the ov-serpin SERPINB3, detected in primary liver cancer but not in normal liver. The aim of the study was to analyse SERPINB3 expression in liver cancer in relation with molecular signatures of poor prognosis and with clinical outcome.
Methods: Liver tumours of 97 patients were analysed in parallel for SERPINB3, TGF-β and β-catenin. In a subgroup of 67 patients with adequate clinical follow-up, the correlation of molecular findings with clinical outcome was also carried out.
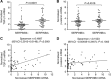
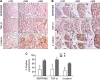
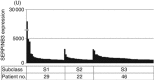
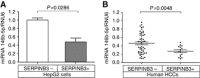
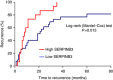
Results: High SERPINB3 levels were detectable in 22% of the patients. A significant correlation of this serpin with TGF-β at transcription and protein level was observed, whereas for β-catenin a strong correlation was found only at post-transcription level. These findings were in agreement with transcriptome data meta-analysis, showing accumulation of SERPINB3 in the poor-prognosis subclass (S1). High levels of this serpin were significantly associated with early tumour recurrence and high SERPINB3 was the only variable significantly associated with time to recurrence at multivariate analysis.
Conclusions: SERPINB3 is overexpressed in the subset of the most aggressive HCCs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SerpinB3 upregulates the Cyclooxygenase-2 / β-Catenin positive loop in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):15732-15743. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14997. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28178650 Free PMC article.
-
SERPINB3 modulates TGF-beta expression in chronic liver disease.Lab Invest. 2010 Jul;90(7):1016-23. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.55. Epub 2010 Mar 8. Lab Invest. 2010. PMID: 20212457
-
SerpinB3 induces dipeptidyl-peptidase IV/CD26 expression and its metabolic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma.Life Sci. 2018 May 1;200:134-141. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29524519
-
Role of SERPINB3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Hepatol. 2014 Nov-Dec;13(6):722-7. Ann Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25332258 Review.
-
MicroRNAs and SerpinB3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Life Sci. 2014 Mar 28;100(1):9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.01.073. Epub 2014 Feb 2. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24496037 Review.
Cited by
-
Low P66shc with High SerpinB3 Levels Favors Necroptosis and Better Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biology (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;10(5):363. doi: 10.3390/biology10050363. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922660 Free PMC article.
-
RNA sequencing-based analysis of gallbladder cancer reveals the importance of the liver X receptor and lipid metabolism in gallbladder cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):35302-12. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9181. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27167107 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory processes involved in NASH-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2023 Jan 31;43(1):BSR20221271. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221271. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36691794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen-Immunoglobulin M complex levels predict survival in patients with cirrhosis.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 27;9(1):20126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56633-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31882893 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-122 Targets SerpinB3 and Is Involved in Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Med. 2019 Feb 1;8(2):171. doi: 10.3390/jcm8020171. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30717317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Sukhun S, Hussain M. Current understanding of the biology of advanced bladder cancer. Cancer. 2003;97:2064–2075. - PubMed
-
- Beneduce L, Castaldi F, Marino M, Quarta S, Ruvoletto M, Benvegnù L, Calabrese F, Gatta A, Pontisso P, Fassina G. Squamous cell carcinoma antigen-immunoglobulin M complexes as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103 (12:2558–2565. - PubMed
-
- Bissell DM, Roulot D, George J. Transforming growth factor beta and the liver. Hepatology. 2001;34:859–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

