Matrix pre-coated targets for high throughput MALDI imaging of proteins
- PMID: 24809903
- PMCID: PMC4028164
- DOI: 10.1002/jms.3354
Matrix pre-coated targets for high throughput MALDI imaging of proteins
Abstract
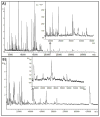
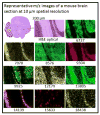
We have developed matrix pre-coated targets for imaging proteins in thin tissue sections by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Gold covered microscope slides were coated with sinapinic acid (SA) in batches in advance and were shown to be stable for over 6 months when kept in the dark. The sample preparation protocol using these SA pre-coated targets involves treatment with diisopropylethylamine (DIEA)-H2 O vapor, transforming the matrix layer to a viscous ionic liquid. This SA-DIEA ionic liquid layer extracts proteins and other analytes from tissue sections that are thaw mounted to this target. DIEA is removed by the immersion of the target into diluted acetic acid, allowing SA to co-crystallize with extracted analytes directly on the target. Ion images (3-70 kDa) of sections of mouse brain and rat kidney at spatial resolution down to 10 µm were obtained. Use of pre-coated slides greatly reduces sample preparation time for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging while providing high throughput, low cost and high spatial resolution images.
Keywords: MALDI IMS; imaging; pre-coated; proteins; target.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Bouschen W, Schulz O, Eikel D, Spengler B. Rapid Commun Mass Sp. 2010;24:355–364. - PubMed
-
- Baluya DL, Garrett TJ, Yost RA. Anal Chem. 2007;79:6862–6867. - PubMed
-
- Aerni HR, Cornett DS, Caprioli RM. Anal Chem. 2005;78:827–834. - PubMed
-
- Sugiura Y, Setou M, Horigome D. In: Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Setou M, editor. Springer; Japan: 2010. pp. 71–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

