Factors associated with early deterioration after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24809990
- PMCID: PMC4014549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096743
Factors associated with early deterioration after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a devastating form of stroke with a poor prognosis overall. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to identify and describe factors associated with early neurologic deterioration (END) after ICH.
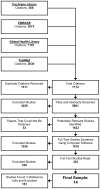
Methods: We sought to identify any factor which could be prognostic in the absence of an intervention. The Cochrane Library, EMBASE, the Global Health Library, and PubMed were searched for primary studies from the years 1966 to 2012 with no restrictions on language or study design. Studies of patients who received a surgical intervention or specific experimental therapies were excluded. END was defined as death, or worsening on a reliable outcome scale within seven days after onset.
Results: 7,172 abstracts were reviewed, 1,579 full-text papers were obtained and screened. 14 studies were identified; including 2088 patients. Indices of ICH severity such as ICH volume (univariate combined OR per ml:1.37, 95%CI: 1.12-1.68), presence of intraventricular hemorrhage (2.95, 95%CI: 1.57-5.55), glucose concentration (per mmol/l: 2.14, 95%CI: 1.03-4.47), fibrinogen concentration (per g/l: 1.83, 95%CI: 1.03-3.25), and d-dimer concentration at hospital admission (per mg/l: 4.19, 95%CI: 1.88-9.34) were significantly associated with END after random-effects analyses. Whereas commonly described risk factors for ICH progression such as blood pressure, history of hypertension, and ICH growth were not.
Conclusions: This study summarizes the evidence to date on early ICH prognosis and highlights that the amount and distribution of the initial bleed at hospital admission may be the most important factors to consider when predicting early clinical outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Qureshi AI, Tuhrim S, Broderick JP, Batjer HH, Hondo H, et al. (2001) Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 344: 1450–1460. - PubMed
-
- Mayer SA, Sacco RL, Shi T, Mohr JP (1994) Neurologic deterioration in noncomatose patients with supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 44: 1379–1384. - PubMed
-
- Qureshi AI, Safdar K, Weil J, Barch C, Bliwise DL, et al. (1995) Predictors of early deterioration and mortality in black Americans with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 26: 1764–1767. - PubMed
-
- Mayer SA, Brun NC, Begtrup K, Broderick J, Davis S, et al. (2008) Efficacy and safety of recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 358: 2127–2137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

