Rapamycin reverses insulin resistance (IR) in high-glucose medium without causing IR in normoglycemic medium
- PMID: 24810050
- PMCID: PMC4047870
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.178
Rapamycin reverses insulin resistance (IR) in high-glucose medium without causing IR in normoglycemic medium
Abstract
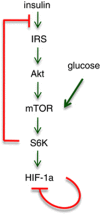
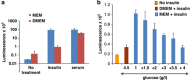
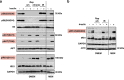
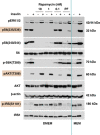
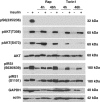
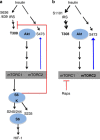
Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is involved in insulin resistance (IR) and diabetic retinopathy. In retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, insulin activates the mTOR pathway, inducing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and HIF-dependent transcription in serum-free minimum essential medium Eagle (MEM). Serendipitously, we found that insulin failed to induce the HIF-1α-dependent response, when RPE cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modification of Eagle's medium (DMEM). Whereas concentration of glucose in MEM corresponds to normal glucose levels in blood (5.5 mM), its concentration in DMEM corresponds to severe diabetic hyperglycemia (25 mM). Addition of glucose to MEM also caused IR. Glucose-mediated IR was characterized by basal activation of mTORC1 and its poor inducibility by insulin. Basal levels of phosphorylated S6 kinase (S6K), S6 and insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) S635/639 were high, whereas their inducibilities were decreased. Insulin-induced Akt phosphorylation was decreased and restored by rapamycin and an inhibitor of S6K. IR was associated with de-phosphorylation of IRS1 at S1011, which was reversed by rapamycin. Both short (16-40 h) and chronic (2 weeks) treatment with rapamycin reversed IR. Furthermore, rapamycin did not impair Akt activation in RPE cells cultured in normoglycemic media. In contrast, Torin 1 blocked Akt activation by insulin. We conclude that by activating mTOR/S6K glucose causes feedback IR, preventable by rapamycin. Rapamycin does not cause IR in RPE cells regardless of the duration of treatment. We confirmed that rapamycin also did not impair phosphorylation of Akt at T308 and S473 in normal myoblast C2C12 cells. Our work provides insights in glucose-induced IR and suggests therapeutic approaches to treat patients with IR and severe hyperglycemia and to prevent diabetic complications such as retinopathy. Also our results prompt to reconsider physiological relevance of numerous data and paradigms on IR given that most cell lines are cultured with grossly super-physiological levels of glucose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serine 302 Phosphorylation of Mouse Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS1) Is Dispensable for Normal Insulin Signaling and Feedback Regulation by Hepatic S6 Kinase.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 15;291(16):8602-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.714915. Epub 2016 Feb 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26846849 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the mTOR/p70S6K pathway is not involved in the insulin-sensitizing effect of AMPK on cardiac glucose uptake.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):H469-77. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00986.2010. Epub 2011 May 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21602475
-
Pharmacological inhibition of S6K1 increases glucose metabolism and Akt signalling in vitro and in diet-induced obese mice.Diabetologia. 2016 Mar;59(3):592-603. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3839-6. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26733005
-
Insulin signaling, resistance, and the metabolic syndrome: insights from mouse models into disease mechanisms.J Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 8;220(2):T1-T23. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0327. Print 2014 Feb. J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24281010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond controlling cell size: functional analyses of S6K in tumorigenesis.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jul 25;13(7):646. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05081-4. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35879299 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UCHL1 regulates muscle fibers and mTORC1 activity in skeletal muscle.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 15;233:116699. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116699. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31356902 Free PMC article.
-
Koschei the immortal and anti-aging drugs.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Dec 4;5(12):e1552. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.520. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25476900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapamycin treatment benefits glucose metabolism in mouse models of type 2 diabetes.Aging (Albany NY). 2016 Nov 30;8(11):3120-3130. doi: 10.18632/aging.101117. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 27922820 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin gallate affects glucose metabolism and increases fitness and lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 13;6(31):30568-78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5215. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26375250 Free PMC article.
-
How the love of muscle can break a heart: Impact of anabolic androgenic steroids on skeletal muscle hypertrophy, metabolic and cardiovascular health.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Jun;22(2):389-405. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09616-y. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 33269425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Luong N, Davies CR, Wessells RJ, Graham SM, King MT, Veech R, et al. Activated FOXO-mediated insulin resistance is blocked by reduction of TOR activity. Cell Metab. 2006;4:133–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

