Epidemiologic features and environmental risk factors of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, Xinyang, China
- PMID: 24810269
- PMCID: PMC4014392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002820
Epidemiologic features and environmental risk factors of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, Xinyang, China
Abstract
Background: Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging infectious disease discovered in rural areas of Central China in 2009, caused by a novel bunyavirus, SFTS virus (SFTSV). The disease usually presents as fever, thrombocytopenia, and leukocytopenia, with case-fatality rates ranging from 2.5% to 30%. Haemaphysalis longicornis was suspected to be the most likely vector of SFTSV. By the end of 2012, the disease had expanded to 13 provinces of China. SFTS patients have been reported in Japan and South Korea, and a disease similar to SFTS has been reported in the United States.
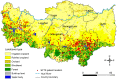
Methodology/principal findings: We characterized the epidemiologic features of 504 confirmed SFTS cases in Xinyang Region, the most severely SFTS-afflicted region in China from 2011 to 2012, and assessed the environmental risk factors. All cases occurred during March to November, with the epidemic peaking from May to July. The patients' ages ranged from 7 to 87 years (median 61 years), and the annual incidence increased with age (χ2 test for trend, P<0.001). The female-to-male ratio of cases was 1.58, and 97.0% of the cases were farmers who resided in the southern and western parts of the region. The Poisson regression analysis revealed that the spatial variations of SFTS incidence were significantly associated with the shrub, forest, and rain-fed cropland areas.
Conclusions: The distribution of SFTS showed highly significant temporal and spatial heterogeneity in Xinyang Region, with the majority of SFTS cases being elderly farmers who resided in the southern and western parts of the region, mostly acquiring infection between May and July when H. longicornis is highly active. The shrub, rain-fed, and rain-fed cropland areas were associated with high risk for this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang YZ, Zhou DJ, Xiong Y, Xiong YW, Chen XP, et al. (2011) Hemorrhagic fever caused by a novel tick-borne bunyavirus in Huaiyangshan, China. Chin J Epidemiol 32: 209–220. - PubMed
-
- Li DX (2011) Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. Chin J Exp Clin Virol 25: 81–84. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health (2010) National guideline for prevention and control of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Beijing: Ministry of Health of People's Republic of China.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

