Inter-species cross-seeding: stability and assembly of rat-human amylin aggregates
- PMID: 24810618
- PMCID: PMC4014569
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097051
Inter-species cross-seeding: stability and assembly of rat-human amylin aggregates
Abstract
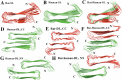
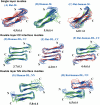
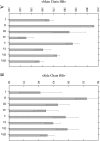
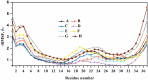
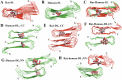
Diseases such as type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's share as common feature the accumulation of mis-folded disease-specific protein aggregates into fibrillar structures, or plaques. These fibrils may either be toxic by themselves, or act as reservoirs for smaller cytotoxic oligomers. This suggests to investigate molecules as potential therapeutics that either reduce fibril formation or increase fibril stability. One example is rat amylin, which can inhibit aggregation of human amylin, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. In the present paper, we use molecular dynamics to compare the stability of various preformed aggregates, built out of either human amylin, rat amylin, or mixtures of both. We considered two types of fibril-like oligomers: a single-layer in-register conformation, and a double-layer conformation in which the first U-shaped layer consists of rat amylin and the second layer of human amylin. Our results explain the weak amyloid-inhibiting properties of rat amylin and suggest that membrane leakage due to pore formation is responsible for the toxicity of rat amylin observed in a recent experiment. Together, our results put in question the use of rat amylin or the similar FDA approved drug pramlintide as an inhibitor of human amylin aggregation. They also point to mixed human-rat amylin fibril-like oligomers as possible model-systems for studies of amyloid formation that involve cross-species transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Full length amylin oligomer aggregation: insights from molecular dynamics simulations and implications for design of aggregation inhibitors.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2014;32(10):1651-69. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2013.832635. Epub 2013 Sep 13. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2014. PMID: 24028418
-
In silico cross seeding of Aβ and amylin fibril-like oligomers.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Nov 20;4(11):1488-500. doi: 10.1021/cn400141x. Epub 2013 Sep 19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24007594 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations and seeding of amylin fibril-like oligomers.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Dec 19;117(50):16076-85. doi: 10.1021/jp409777p. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 24294935 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid fibril toxicity in Alzheimer's disease and diabetes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996 Jan 17;777:89-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb34406.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. PMID: 8624132 Review.
-
Human Amylin: From Pathology to Physiology and Pharmacology.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(9):944-957. doi: 10.2174/1389203720666190328111833. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019. PMID: 30919775 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying the Role of Individual Seal IAPP Amino Acids in Inhibiting the Aggregation of Human IAPP.Protein Pept Lett. 2025;32(1):44-53. doi: 10.2174/0109298665340227241115110404. Protein Pept Lett. 2025. PMID: 39660516
-
On the lack of polymorphism in Aβ-peptide aggregates derived from patient brains.Protein Sci. 2015 Jun;24(6):923-35. doi: 10.1002/pro.2668. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25739352 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Modulation in the Formation of β-Sheet Structures. Implications for De Novo Design of Human Islet Amyloid Polypeptide and the Impact on β-Cell Homeostasis.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 19;10(9):1201. doi: 10.3390/biom10091201. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32824918 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Amyloidogenesis Controlled by the C-Terminal Domain of Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Shows New Functions on Hepatocyte Cholesterol Metabolism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jun 25;9:331. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00331. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29988450 Free PMC article.
-
Nonhuman IAPP Variants Inhibit Human IAPP Aggregation.Protein Pept Lett. 2021;28(9):963-971. doi: 10.2174/0929866528666210806152706. Protein Pept Lett. 2021. PMID: 34365921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lorenzo A, Razzaboni B, Weir GC, Yankner BA (1994) Pancreatic-islet cell toxicity of amylin associated with type-2 diabetes-mellitus. Nature 368: 756–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

