Erythema multiforme after orf virus infection: a report of two cases and literature review
- PMID: 24810660
- PMCID: PMC9206774
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268814000879
Erythema multiforme after orf virus infection: a report of two cases and literature review
Abstract
Orf virus has a worldwide distribution among sheep and goats. The hypersensitivity reaction erythema multiforme (EM) is a known complication of orf infection in humans; however, its occurrence is poorly understood and has not been extensively reviewed. We present two unrelated cases of orf-associated EM, and a review of the literature, highlighting important clinical, epidemiological and immunological aspects of this condition. Orf and its associated complications can occur in rural areas, as well as urban settings, where it is less well-known, through religious or cultural practices involving animal slaughter. Obtaining a history of animal exposures from patients with lesions suspicious for orf and secondary skin eruptions can guide diagnosis and identification of the inciting immune stimulus. Determining the pathophysiology and relative contribution of host and viral factors contributing to EM and other orf-associated hypersensitivity reactions could facilitate the identification of risk factors and inform treatment decisions.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

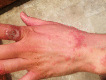
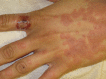
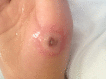
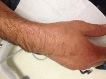
Similar articles
-
Erythema multiforme after orf virus infection.Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jul;35(4):e237-e238. doi: 10.1111/pde.13526. Epub 2018 May 15. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29766553
-
Finger nodules with a papulovesicular hands and feet eruption: a complicated human Orf virus infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 17;24(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-08998-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38229010 Free PMC article.
-
[Orf parapoxvirus can infect humans after relevant exposure].Ugeskr Laeger. 2013 Apr 15;175(16):1121-2. Ugeskr Laeger. 2013. PMID: 23651755 Danish.
-
Orf Virus in Humans: Case Series and Clinical Review.Cutis. 2022 Jul;110(1):48-52. doi: 10.12788/cutis.0567. Cutis. 2022. PMID: 36179231 Review.
-
An Overwiev of ORF Virus Infection in Humans and Animals.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2017;12(1):21-30. doi: 10.2174/1574891X12666170602080301. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28571550 Review.
Cited by
-
Orf (Ecthyma Contagiosum) Transmitted from a Camel to a Human: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Dec 23;21:e927579. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.927579. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33353926 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Orf Identified by Transmission Electron Microscopy.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jan 5;129(1):108-9. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.172606. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 26712444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Review on Human Orf: A Neglected Viral Zoonosis.Res Rep Trop Med. 2021 Jul 8;12:153-172. doi: 10.2147/RRTM.S306446. eCollection 2021. Res Rep Trop Med. 2021. PMID: 34267574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 65-Year-Old Female from Connecticut with Orf Infection.Dermatopathology (Basel). 2016 Jun 22;3(2):55-60. doi: 10.1159/000447125. eCollection 2016 Apr-Jun. Dermatopathology (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27504446 Free PMC article.
-
A case of orf disease in a patient with scleroderma.JAAD Case Rep. 2017 Mar 22;3(2):155-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2017.01.015. eCollection 2017 Mar. JAAD Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28374002 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Haig DM, et al. Orf virus immuno-modulation and the host immune response. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 2002; 87: 395–399. - PubMed
-
- Diven DG. An overview of poxviruses. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2001; 4: 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Human orf virus infection from household exposures – United States, 2009–2011. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2012; 61: 245–248. - PubMed
-
- Robinson AJ, Peterson GV. Orf virus infection of workers in the meat industry. New Zealand Medical Journal 1983; 96: 81–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

