Enhanced interaction between pseudokinase and kinase domains in Gcn2 stimulates eIF2α phosphorylation in starved cells
- PMID: 24811037
- PMCID: PMC4014428
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004326
Enhanced interaction between pseudokinase and kinase domains in Gcn2 stimulates eIF2α phosphorylation in starved cells
Abstract
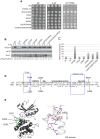
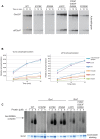
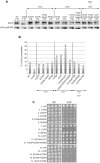
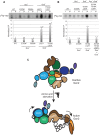
The stress-activated protein kinase Gcn2 regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF2α, from yeast to mammals. The Gcn2 kinase domain (KD) is inherently inactive and requires allosteric stimulation by adjoining regulatory domains. Gcn2 contains a pseudokinase domain (YKD) required for high-level eIF2α phosphorylation in amino acid starved yeast cells; however, the role of the YKD in KD activation was unknown. We isolated substitutions of evolutionarily conserved YKD amino acids that impair Gcn2 activation without reducing binding of the activating ligand, uncharged tRNA, to the histidyl-tRNA synthetase-related domain of Gcn2. Several such Gcn- substitutions cluster in predicted helices E and I (αE and αI) of the YKD. We also identified Gcd- substitutions, evoking constitutive activation of Gcn2, mapping in αI of the YKD. Interestingly, αI Gcd- substitutions enhance YKD-KD interactions in vitro, whereas Gcn- substitutions in αE and αI suppress both this effect and the constitutive activation of Gcn2 conferred by YKD Gcd- substitutions. These findings indicate that the YKD interacts directly with the KD for activation of kinase function and identify likely sites of direct YKD-KD contact. We propose that tRNA binding to the HisRS domain evokes a conformational change that increases access of the YKD to sites of allosteric activation in the adjoining KD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Purification and Analysis of eIF2α Phosphorylation by Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Gcn2 from S. cerevisiae.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2882:195-220. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4284-9_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39992511
-
Interaction between the tRNA-binding and C-terminal domains of Yeast Gcn2 regulates kinase activity in vivo.PLoS Genet. 2015 Feb 19;11(2):e1004991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004991. eCollection 2015 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25695491 Free PMC article.
-
A network of hydrophobic residues impeding helix alphaC rotation maintains latency of kinase Gcn2, which phosphorylates the alpha subunit of translation initiation factor 2.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Mar;29(6):1592-607. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01446-08. Epub 2008 Dec 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19114556 Free PMC article.
-
New functions of protein kinase Gcn2 in yeast and mammals.IUBMB Life. 2012 Dec;64(12):971-4. doi: 10.1002/iub.1090. Epub 2012 Nov 5. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 23129244 Review.
-
Regulation of translation initiation by amino acids in eukaryotic cells.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2001;26:155-84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56688-2_6. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11575165 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM structure of histidyl-tRNA synthetase-like domain reveals activating crossed helices at the core of GCN2.PNAS Nexus. 2024 Nov 21;3(12):pgae528. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae528. eCollection 2024 Dec. PNAS Nexus. 2024. PMID: 39618511 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Analysis of eIF2α Phosphorylation by Stress-Activated Protein Kinase Gcn2 from S. cerevisiae.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2882:195-220. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4284-9_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39992511
-
Mechanism and Regulation of Protein Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):65-107. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186221. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27183566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast as a Model to Understand Actin-Mediated Cellular Functions in Mammals-Illustrated with Four Actin Cytoskeleton Proteins.Cells. 2020 Mar 10;9(3):672. doi: 10.3390/cells9030672. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32164332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A GCN2-Like eIF2α Kinase (LdeK1) of Leishmania donovani and Its Possible Role in Stress Response.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 1;11(6):e0156032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156032. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27248816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hinnebusch AG (2005) Translational regulation of GCN4 and the general amino acid control of yeast. Annu Rev Microbiol 59: 407–450. - PubMed
-
- Guo F, Cavener DR (2007) The GCN2 eIF2α kinase regulates fatty-acid homeostasis in the liver during deprivation of an essential amino acid. Cell Metab 5: 103–114. - PubMed
-
- Hao S, Sharp JW, Ross-Inta CM, McDaniel BJ, Anthony TG, et al. (2005) Uncharged tRNA and sensing of amino acid deficiency in mammalian piriform cortex. Science 307: 1776–1778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

