Transmitting pain and itch messages: a contemporary view of the spinal cord circuits that generate gate control
- PMID: 24811377
- PMCID: PMC4492533
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.018
Transmitting pain and itch messages: a contemporary view of the spinal cord circuits that generate gate control
Abstract
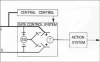
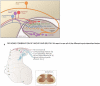
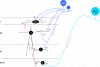
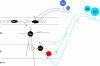
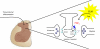
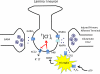
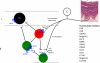
The original formulation of Gate Control Theory (GCT) proposed that the perception of pain produced by spinal cord signaling to the brain depends on a balance of activity generated in large (nonnociceptive)- and small (nociceptive)-diameter primary afferent fibers. The theory proposed that activation of the large-diameter afferent "closes" the gate by engaging a superficial dorsal horn interneuron that inhibits the firing of projection neurons. Activation of the nociceptors "opens" the gate through concomitant excitation of projection neurons and inhibition of the inhibitory interneurons. Sixty years after publication of the GCT, we are faced with an ever-growing list of morphologically and neurochemically distinct spinal cord interneurons. The present Review highlights the complexity of superficial dorsal horn circuitry and addresses the question whether the premises outlined in GCT still have relevance today. By examining the dorsal horn circuits that underlie the transmission of "pain" and "itch" messages, we also address the extent to which labeled lines can be incorporated into a contemporary view of GCT.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmadi S, Lippross S, Neuhuber WL, Zeilhofer HU. PGE(2) selectively blocks inhibitory glycinergic neurotransmission onto rat superficial dorsal horn neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque C, Lee CJ, Jackson AC, MacDermott AB. Subpopulations of GABAergic and non-GABAergic rat dorsal horn neurons express Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2758–2766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

