Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized following pulmonary aspiration
- PMID: 24811480
- PMCID: PMC4188146
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.13-3028
Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized following pulmonary aspiration
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary aspiration is an important recognized cause of ARDS. Better characterization of patients who aspirate may allow identification of potential risks for aspiration that could be used in future studies to mitigate the occurrence of aspiration and its devastating complications.
Methods: We conducted a secondary analysis of the Lung Injury Prediction Score cohort to better characterize patients with aspiration, including their potential risk factors and related outcomes.
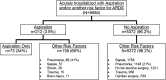
Results: Of the 5,584 subjects at risk for ARDS and who required hospitalization, 212 (3.8%) presented with aspiration. Subjects who aspirated were likely to be male (66% vs 56%, P < .007), slightly older (59 years vs 57 years), white (73% vs 61%, P = .0004), admitted from a nursing home (15% vs 5.9%, P < .0001), have a history of alcohol abuse (21% vs 8%, P < .0001), and have lower Glasgow Coma Scale (median, 13 vs 15; P < .0001). Aspiration subjects were sicker (higher APACHE [Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation] II score), required more mechanical ventilation (54% vs 32%, P < .0001), developed more moderate to severe ARDS (12% vs 3.8%, P < .0001), and were twofold more likely to die in-hospital, even after adjustment for severity of illness (OR = 2.1; 95% CI, 1.2-3.6). Neither obesity nor gastroesophageal reflux was associated with aspiration.
Conclusions: Aspiration was more common in men with alcohol abuse history and a lower Glasgow Coma Scale who were admitted from a nursing home. It is independently associated with a significant increase in the risk for ARDS as well as morbidity and mortality. Findings from this study may facilitate the design of future clinical studies of aspiration-induced lung injury.
Figures
References
-
- Pepe PE, Potkin RT, Reus DH, Hudson LD, Carrico CJ. Clinical predictors of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Surg. 1982;144(1):124-130 - PubMed
-
- Fowler AA, Hamman RF, Good JT, et al. Adult respiratory distress syndrome: risk with common predispositions. Ann Intern Med. 1983;98(5 Pt 1):593-597 - PubMed
-
- Doyle RL, Szaflarski N, Modin GW, Wiener-Kronish JP, Matthay MA. Identification of patients with acute lung injury. Predictors of mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152(6 Pt 1):1818-1824 - PubMed
-
- Zilberberg MD, Epstein SK. Acute lung injury in the medical ICU: comorbid conditions, age, etiology, and hospital outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(4 Pt 1):1159-1164 - PubMed
-
- Eisner MD, Thompson T, Hudson LD, et al. ; Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Efficacy of low tidal volume ventilation in patients with different clinical risk factors for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164(2):231-236 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

