Enhanced protein degradation by branched ubiquitin chains
- PMID: 24813613
- PMCID: PMC4028144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.037
Enhanced protein degradation by branched ubiquitin chains
Abstract
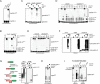
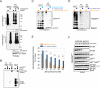
Posttranslational modification of cell-cycle regulators with ubiquitin chains is essential for eukaryotic cell division. Such chains can be connected through seven lysine residues or the amino terminus of ubiquitin, thereby allowing the assembly of eight homogenous and multiple mixed or branched conjugates. Although functions of homogenous chain types have been described, physiological roles of branched structures are unknown. Here, we report that the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) efficiently synthesizes branched conjugates that contain multiple blocks of K11-linked chains. Compared to homogenous chains, the branched conjugates assembled by the APC/C strongly enhance substrate recognition by the proteasome, thereby driving degradation of cell-cycle regulators during early mitosis. Our work, therefore, identifies an enzyme and substrates for modification with branched ubiquitin chains and points to an important role of these conjugates in providing an improved signal for proteasomal degradation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Deciphering functions of branched ubiquitin chains.Cell. 2014 May 8;157(4):767-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.026. Cell. 2014. PMID: 24813601
References
-
- Chau V, Tobias JW, Bachmair A, Marriott D, Ecker DJ, Gonda DK, Varshavsky A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science. 1989;243:1576–1583. - PubMed
-
- Deshaies RJ, Joazeiro CA. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:399–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

