In vivo endothelial siRNA delivery using polymeric nanoparticles with low molecular weight
- PMID: 24813696
- PMCID: PMC4207430
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2014.84
In vivo endothelial siRNA delivery using polymeric nanoparticles with low molecular weight
Abstract
Dysfunctional endothelium contributes to more diseases than any other tissue in the body. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can help in the study and treatment of endothelial cells in vivo by durably silencing multiple genes simultaneously, but efficient siRNA delivery has so far remained challenging. Here, we show that polymeric nanoparticles made of low-molecular-weight polyamines and lipids can deliver siRNA to endothelial cells with high efficiency, thereby facilitating the simultaneous silencing of multiple endothelial genes in vivo. Unlike lipid or lipid-like nanoparticles, this formulation does not significantly reduce gene expression in hepatocytes or immune cells even at the dosage necessary for endothelial gene silencing. These nanoparticles mediate the most durable non-liver silencing reported so far and facilitate the delivery of siRNAs that modify endothelial function in mouse models of vascular permeability, emphysema, primary tumour growth and metastasis.
Figures
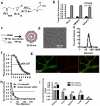
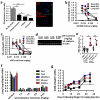

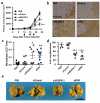
Comment in
-
Gene delivery: cell-specific therapy on target.Nat Nanotechnol. 2014 Aug;9(8):568-9. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.155. Nat Nanotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25091443 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pober JS, Sessa WC. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:803–815. - PubMed
-
- Hagberg CE, et al. Targeting VEGF-B as a novel treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2012;490:426–430. - PubMed
-
- Kumar V, Abbas A, Fausto N, Aster J. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. (Eighth Edition) 2009
-
- Kanasty R, Dorkin JR, Vegas A, Anderson D. Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics. Nat Mater. 2013;12:967–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

