Life extension factor klotho enhances cognition
- PMID: 24813892
- PMCID: PMC4176932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.03.076
Life extension factor klotho enhances cognition
Abstract
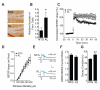
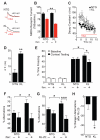
Aging is the primary risk factor for cognitive decline, an emerging health threat to aging societies worldwide. Whether anti-aging factors such as klotho can counteract cognitive decline is unknown. We show that a lifespan-extending variant of the human KLOTHO gene, KL-VS, is associated with enhanced cognition in heterozygous carriers. Because this allele increased klotho levels in serum, we analyzed transgenic mice with systemic overexpression of klotho. They performed better than controls in multiple tests of learning and memory. Elevating klotho in mice also enhanced long-term potentiation, a form of synaptic plasticity, and enriched synaptic GluN2B, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) subunit with key functions in learning and memory. Blockade of GluN2B abolished klotho-mediated effects. Surprisingly, klotho effects were evident also in young mice and did not correlate with age in humans, suggesting independence from the aging process. Augmenting klotho or its effects may enhance cognition and counteract cognitive deficits at different life stages.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
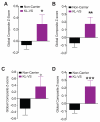

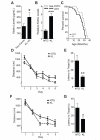
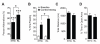
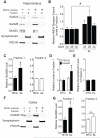
Comment in
-
Cognition: Klotho spins cognitive fate.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Jul;15(7):425. doi: 10.1038/nrn3777. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24938722 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arking DE, Atzmon G, Arking A, Barzilai N, Dietz HC. Association between a functional variant of the KLOTHO gene and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, blood pressure, stroke, and longevity. Circ Res. 2005;96:412–418. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science. 1993;260:181–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG17917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019712/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG032289/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG00001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG010435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS065780/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG19724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG025831/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG025831/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG040127/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG032289/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG010435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AG034531/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG23501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS065780/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG000001/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG15819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG019712/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG022074/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG18440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032289/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG034531/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RR18938-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

