Behavioral and cellular pharmacology characterization of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-(isoquinoline-3'-carboxamido)morphinan (NAQ) as a mu opioid receptor selective ligand
- PMID: 24815322
- PMCID: PMC4073486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.04.041
Behavioral and cellular pharmacology characterization of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-(isoquinoline-3'-carboxamido)morphinan (NAQ) as a mu opioid receptor selective ligand
Abstract
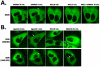
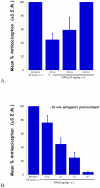
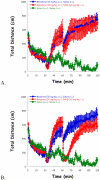
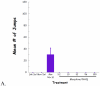
Mu opioid receptor (MOR) selective antagonists and partial agonists have been used for the treatment of opioid abuse and addiction. Our recent efforts on the identification of MOR antagonists have provided several novel leads displaying interesting pharmacological profiles. Among them, 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-[(3'-isoquinolyl)acetamido]morphinan (NAQ) showed sub-nanomolar binding affinity to the MOR with significant selectivity over the delta opioid receptor (DOR) and the kappa opioid receptor (KOR). Its central nervous system penetration capacity together with marginal agonism in the MOR-GTPγS binding assay made it a very interesting molecule for developing novel opioid abuse and addiction therapeutic agents. Therefore, further pharmacological characterization was conducted to fully understand its biological profile. At the molecular and cellular level, NAQ not only induced no translocation of β-arrestin2 to the MOR, but also efficaciously antagonized the effect of DAMGO in MOR-βarr2eGFP-U2OS cells in the β-arrestin2 recruitment assay. At the in vivo level, NAQ displayed a potent inhibition of the analgesic effect of morphine in the tail-flick assay (ID50=1.19 mg/kg). NAQ (10 mg/kg) also significantly decreased the hyper-locomotion induced by acute morphine without inducing any vertical jumps. Meanwhile NAQ precipitated lesser withdrawal symptoms in morphine dependent mice than naloxone. In conclusion, NAQ may represent a new chemical entity for opioid abuse and addiction treatment.
Keywords: Antagonist; Mu opioid receptor; NAQ; Pharmacology; in vitro; in vivo.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo functional profile characterization of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-(isoquinoline-3-carboxamido)morphinan (NAQ) as a low efficacy mu opioid receptor modulator.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 May 15;827:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29530590 Free PMC article.
-
Design, syntheses, and pharmacological characterization of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-(isoquinoline-3'-carboxamido)morphinan analogues as opioid receptor ligands.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Apr 15;23(8):1701-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.02.055. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25783191 Free PMC article.
-
Structure activity relationship studies of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-(isoquinoline-3'-carboxamido)morphinan (NAQ) analogues as potent opioid receptor ligands: preliminary results on the role of electronic characteristics for affinity and function.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Sep 15;23(18):5045-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.07.043. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 23948248 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-Free Signaling of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Relevance to μ Opioid Receptors in Analgesia and Addiction.Molecules. 2022 Sep 8;27(18):5826. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185826. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diels-Alder Adducts of Morphinan-6,8-Dienes and Their Transformations.Molecules. 2022 Apr 30;27(9):2863. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092863. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
17-Cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6β-(4'-pyridylcarboxamido)morphinan (NAP) Modulating the Mu Opioid Receptor in a Biased Fashion.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Mar 16;7(3):297-304. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00245. Epub 2016 Jan 8. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26716358 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo functional profile characterization of 17-cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6α-(isoquinoline-3-carboxamido)morphinan (NAQ) as a low efficacy mu opioid receptor modulator.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 May 15;827:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29530590 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of a dual kappa-delta opioid receptor agonist analgesic blocking cocaine reward behavior.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Nov 18;6(11):1813-24. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00153. Epub 2015 Sep 14. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26325040 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Characterization and Development on NAQ as a Mu Opioid Receptor Partial Agonist for Opioid Use Disorder Treatment.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Nov 2;5(11):1197-1209. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00178. eCollection 2022 Nov 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407950 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive Interactions between the Imidazoline I2 Receptor Agonist 2-BFI and Opioids in Rats: Role of Efficacy at the μ-Opioid Receptor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Jun;357(3):509-19. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.232421. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 27056847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Salam OM. Antinociceptive and behavioral effects of ribavirin in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006;83:230–238. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez V, Arttamangkul S, Williams JT. A RAVE about opioid withdrawal. Neuron. 2001;32:761–763. - PubMed
-
- Baamonde A, Daugé V, Ruiz-Gayo M, Fulga IG, Turcaud S, Fournié-Zaluski MC, Roques BP. Antidepressant-type effects of endogenous enkephalins protected by systemic RB 101 are mediated by opioid delta and dopamine D1 receptor stimulation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992;216:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Barak LS, Ferguson SS, Zhang J, Caron MG. A beta-arrestin/green fluorescent protein biosensor for detecting G protein-coupled receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:27497–27500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

