Mitochondrial oxidant stress in locus coeruleus is regulated by activity and nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 24816140
- PMCID: PMC4131291
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3717
Mitochondrial oxidant stress in locus coeruleus is regulated by activity and nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
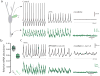
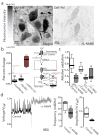
Loss of noradrenergic locus coeruleus (LC) neurons is a prominent feature of aging-related neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease (PD). The basis of this vulnerability is not understood. To explore possible physiological determinants, we studied LC neurons using electrophysiological and optical approaches in ex vivo mouse brain slices. We found that autonomous activity in LC neurons was accompanied by oscillations in dendritic Ca(2+) concentration that were attributable to the opening of L-type Ca(2+) channels. This oscillation elevated mitochondrial oxidant stress and was attenuated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. The relationship between activity and stress was malleable, as arousal and carbon dioxide increased the spike rate but differentially affected mitochondrial oxidant stress. Oxidant stress was also increased in an animal model of PD. Thus, our results point to activity-dependent Ca(2+) entry and a resulting mitochondrial oxidant stress as factors contributing to the vulnerability of LC neurons.
Figures
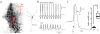




Comment in
-
Pacemaker's burden.Nat Neurosci. 2014 Jun;17(6):755. doi: 10.1038/nn0614-755. Nat Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24866040 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aston–Jones G, Cohen JD. An integrative theory of locus coeruleus–norepinephrine function: adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:403–450. - PubMed
-
- Sara SJ. The locus coeruleus and noradrenergic modulation of cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:211–223. - PubMed
-
- Park A, Stacy M. Non–motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. 2009;256(Suppl 3):293–298. - PubMed
-
- Nicholls DG. Oxidative stress and energy crises in neuronal dysfunction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1147:53–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

