Aurora-A mitotic kinase induces endocrine resistance through down-regulation of ERα expression in initially ERα+ breast cancer cells
- PMID: 24816249
- PMCID: PMC4016211
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096995
Aurora-A mitotic kinase induces endocrine resistance through down-regulation of ERα expression in initially ERα+ breast cancer cells
Abstract
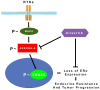
Development of endocrine resistance during tumor progression represents a major challenge in the management of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) positive breast tumors and is an area under intense investigation. Although the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood, many studies point towards the 'cross-talk' between ERα and MAPK signaling pathways as a key oncogenic axis responsible for the development of estrogen-independent growth of breast cancer cells that are initially ERα+ and hormone sensitive. In this study we employed a metastatic breast cancer xenograft model harboring constitutive activation of Raf-1 oncogenic signaling to investigate the mechanistic linkage between aberrant MAPK activity and development of endocrine resistance through abrogation of the ERα signaling axis. We demonstrate for the first time the causal role of the Aurora-A mitotic kinase in the development of endocrine resistance through activation of SMAD5 nuclear signaling and down-regulation of ERα expression in initially ERα+ breast cancer cells. This contribution is highly significant for the treatment of endocrine refractory breast carcinomas, because it may lead to the development of novel molecular therapies targeting the Aurora-A/SMAD5 oncogenic axis. We postulate such therapy to result in the selective eradication of endocrine resistant ERαlow/- cancer cells from the bulk tumor with consequent benefits for breast cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
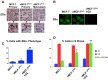
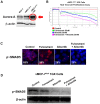
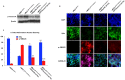
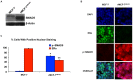
Similar articles
-
The mitotic kinase Aurora--a promotes distant metastases by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ERα(+) breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2014 Jan 30;33(5):599-610. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.628. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23334326 Free PMC article.
-
AKT3 regulates ErbB2, ErbB3 and estrogen receptor α expression and contributes to endocrine therapy resistance of ErbB2(+) breast tumor cells from Balb-neuT mice.Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):1021-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.018. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24463007
-
Aurora-A is a determinant of tamoxifen sensitivity through phosphorylation of ERα in breast cancer.Oncogene. 2014 Oct 16;33(42):4985-96. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.444. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Oncogene. 2014. Retraction in: Oncogene. 2024 Apr;43(15):1160. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02983-9. PMID: 24166501 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Dual-target inhibitors based on ERα: Novel therapeutic approaches for endocrine resistant breast cancer.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Apr 15;270:116393. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116393. Epub 2024 Apr 7. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38588626 Review.
-
Targeting estrogen receptor α for degradation with PROTACs: A promising approach to overcome endocrine resistance.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Nov 15;206:112689. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112689. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32829249 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Regulatory Potential of Antioxidant and Electron-Shuttling Bioactive Compounds in Oolong Tea.Biology (Basel). 2025 Apr 28;14(5):487. doi: 10.3390/biology14050487. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427676 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Significance of Aurora Kinases-p53 Protein Family Interactions in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2016 Nov 25;6:247. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00247. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27933271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tank Binding Kinase 1 modulates spindle assembly checkpoint components to regulate mitosis in breast and lung cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021 Mar;1868(3):118929. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118929. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33310066 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jan;48(1):915-925. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06100-3. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33409716 Review.
-
Seize the engine: Emerging cell cycle targets in breast cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Jan;14(1):e1544. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1544. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38264947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li CI, Daling JR, Malone KE (2003) Incidence of invasive breast cancer by hormone receptor status from 1992 to 1998. J Clin Oncol 21(1): 28–34. - PubMed
-
- Colleoni M, Sun Z, Martinelli G, Basser RL, Coates AS, et al. (2009) The effect of endocrine responsiveness on high-risk breast cancer treated with dose-intensive chemotherapy: results of International Breast Cancer Study Group Trial 15–95 after prolonged follow-up. International Breast Cancer Study Group. Ann Oncol 20(8): 1344–51. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ring A, Dowsett M (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer 11(4): 643–58. - PubMed
-
- Di Leo A, Malorni L (2012) Polyendocrine treatment in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: a “FACT” yet to be proven. J Clin Oncol 30(16): 1897–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

