Three dimensional cellular microarray platform for human neural stem cell differentiation and toxicology
- PMID: 24816401
- PMCID: PMC4090259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2014.04.004
Three dimensional cellular microarray platform for human neural stem cell differentiation and toxicology
Abstract
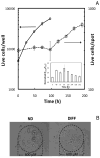
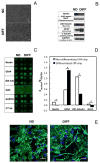
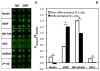
We developed a three-dimensional (3D) cellular microarray platform for the high-throughput (HT) analysis of human neural stem cell (hNSC) growth and differentiation. The growth of an immortalized hNSC line, ReNcell VM, was evaluated on a miniaturized cell culture chip consisting of 60nl spots of cells encapsulated in alginate, and compared to standard 2D well plate culture conditions. Using a live/dead cell viability assay, we demonstrated that the hNSCs are able to expand on-chip, albeit with lower proliferation rates and viabilities than in conventional 2D culture platforms. Using an in-cell, on-chip immunofluorescence assay, which provides quantitative information on cellular levels of proteins involved in neural fate, we demonstrated that ReNcell VM can preserve its multipotent state during on-chip expansion. Moreover, differentiation of the hNSCs into glial progeny was achieved both off- and on-chip six days after growth factor removal, accompanied by a decrease in the neural progenitor markers. The versatility of the platform was further demonstrated by complementing the cell culture chip with a chamber system that allowed us to screen for differential toxicity of small molecules to hNSCs. Using this approach, we showed differential toxicity when evaluating three neurotoxic compounds and one antiproliferative compound, and the null effect of a non-toxic compound at relevant concentrations. Thus, our 3D high-throughput microarray platform may help predict, in vitro, which compounds pose an increased threat to neural development and should therefore be prioritized for further screening and evaluation.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Adams J, Lammer EJ. Relationship between dysmorphology and neuropsychological function in children exposed to isotretinoin “in utero”. In: Fujii T, Boer CJ, editors. Functional Neuroteratology of Short-Term Exposure to Drugs. Tokyo: Teikyo University Press; 1991. pp. 59–70.
-
- Andersen ME, Krewski D. Toxicity testing in the 21st century: bringing the vision to life. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology. 2009;107(2):324–30. - PubMed
-
- Ashton RS, et al. Scaffolds based on degradable alginate hydrogels and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for stem cell culture. Biomaterials. 2007;28(36):5518–5525. - PubMed
-
- Bal-Price AK, et al. Relevance of in vitro neurotoxicity testing for regulatory requirements: challenges to be considered. Neurotoxicology and teratology. 2010;32(1):36–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

