Sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization versus transarterial chemoembolization alone for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching study
- PMID: 24817002
- PMCID: PMC4016022
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096620
Sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization versus transarterial chemoembolization alone for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching study
Abstract
Aims: The purpose of the present study was to compare the efficacies of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with sorafenib versus TACE monotherapy for treating patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
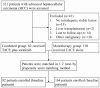
Methods: We enrolled 321 patients and selected 280 with advanced HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C) who underwent TACE therapy between February 2009 and February 2013. TACE alone (monotherapy group) was administered to 198 patients (70.7%), and the remaining 82 (29.3%) underwent repeat combined TACE and sorafenib therapy (combined group). To minimize selection bias, these latter 82 patients were matched using propensity-score matching at a 1∶2 ratio with 164 patients who received TACE monotherapy. The primary endpoints were overall survival (OS) and related subgroup analysis. The secondary endpoints were time to progression (TTP) and treatment-related adverse events.
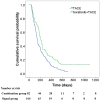
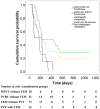
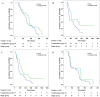
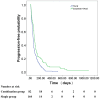
Results: Of the respective patients in the combined and monotherapy groups, 64.6% and 49.2% had vascular invasion, 87.8% and 91.1% had extrahepatic metastasis, and 54.3% and 47.1% had both. In the propensity-score-matched cohort, the OS survival of the combined group was significantly higher compared with the monotherapy group (7.0 months vs. 4.9 months, respectively, P = 0.003). The TTP was significantly longer in the combined group (2.6 months vs. 1.9 months, respectively, P = 0.001). Subgroup analysis showed that the outcomes of patients with advanced HCC without main portal vein invasion who were treated with combined therapy were significantly better compared with those who received monotherapy (P<0.05). Univariate and subsequent multivariate analyses revealed that the addition of sorafenib was an independent predictor of favorable OS and TTP (adjusted hazard ratios, 0.63 and 0.62, respectively; P<0.05 for both).
Conclusion: Sorafenib plus TACE was more effective than TACE monotherapy for treating patients with advanced HCC without main portal vein invasion. Future trials with larger samples are required to validate these preliminary findings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sorafenib alone versus sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization for advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: results of propensity score analyses.Radiology. 2013 Nov;269(2):603-11. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13130150. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Radiology. 2013. PMID: 23864102
-
Sorafenib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization improves the survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching study.J Dig Dis. 2013 Apr;14(4):181-90. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12038. J Dig Dis. 2013. PMID: 23324079 Clinical Trial.
-
Retrospective analysis of transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib in Chinese patients with unresectable and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):83806-83816. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11514. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27566566 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Oct;41(10):6575-82. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3541-7. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25091939
-
Transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib for the management of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep 4;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12876-018-0849-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30180810 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Sorafenib in Patients with BCLC Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Aug 25;14:3461-3468. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S248850. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32904650 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib in Combination with TACE.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Jun 1;21(6):1797-1805. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.6.1797. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32592380 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Analysis of Efficacy of Apatinib Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization and Transarterial Chemoembolization Alone in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus.J Oncol. 2022 Mar 21;2022:1255133. doi: 10.1155/2022/1255133. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35356254 Free PMC article.
-
Survival benefit of transarterial chemoembolization in patients with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma: a single center experience.BMC Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 10;17(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12876-017-0656-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28797231 Free PMC article.
-
Locoregional Therapy Approaches for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Recent Advances and Management Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 15;12(7):1914. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071914. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32679897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Mason AC (1999) Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med 340: 745–750. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94: 153–156. - PubMed
-
- Liao M, Huang J, Zhang T, Wu H (2013) Transarterial chemoembolization in combination with local therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8(7): e68453 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068453 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Takayasu K, Arii S, Ikai I, Omata M, Okita K, et al. (2006) Prospective cohort study of transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in 8510 patients. Gastroenterology 131: 461–469. - PubMed
-
- Takayasu K, Arii S, Ikai I, Kudo M, Matsuyama Y, et al. (2010) Overall survival after transarterial lipiodol infusion chemotherapy with or without embolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: propensity score analysis. Am J Roentgenol 194: 830–837. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

