Costing hospital surgery services: the method matters
- PMID: 24817167
- PMCID: PMC4016301
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097290
Costing hospital surgery services: the method matters
Abstract
Background: Accurate hospital costs are required for policy-makers, hospital managers and clinicians to improve efficiency and transparency. However, different methods are used to allocate direct costs, and their agreement is poorly understood. The aim of this study was to assess the agreement between bottom-up and top-down unit costs of a large sample of surgical operations in a French tertiary centre.
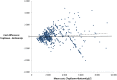
Methods: Two thousand one hundred and thirty consecutive procedures performed between January and October 2010 were analysed. Top-down costs were based on pre-determined weights, while bottom-up costs were calculated through an activity-based costing (ABC) model. The agreement was assessed using correlation coefficients and the Bland and Altman method. Variables associated with the difference between methods were identified with bivariate and multivariate linear regressions.
Results: The correlation coefficient amounted to 0.73 (95%CI: 0.72; 0.76). The overall agreement between methods was poor. In a multivariate analysis, the cost difference was independently associated with age (Beta = -2.4; p = 0.02), ASA score (Beta = 76.3; p<0.001), RCI (Beta = 5.5; p<0.001), staffing level (Beta = 437.0; p<0.001) and intervention duration (Beta = -10.5; p<0.001).
Conclusions: The ability of the current method to provide relevant information to managers, clinicians and payers is questionable. As in other European countries, a shift towards time-driven activity-based costing should be advocated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Busse R, Geissler A, Quentin W, Wiley M (2011) Diagnosis-Related groups in Europe. Moving towards transparency, efficiency and quality in hospitals. Copenhagen: Open University Press. - PubMed
-
- Shleifer A (1985) A Theory of Yardstick Competition. The RAND Journal of Economics 16: 319.
-
- Finkler S, Ward D, Baker J (2007) Essentials of Cost Accounting for Health Care Organizations. New York: Aspen publishers.
-
- Porter ME (2010) What is value in health care? N Engl J Med 363: 2477–2481. - PubMed
-
- Vogl M (2013) Improving patient-level costing in the English and the German ‘DRG’ system. Health Policy 109: 290–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials