Oral complications in hematopoietic stem cell recipients: the role of inflammation
- PMID: 24817792
- PMCID: PMC4003795
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/378281
Oral complications in hematopoietic stem cell recipients: the role of inflammation
Abstract
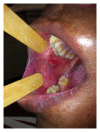
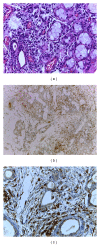
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is widely used as a potentially curative treatment for patients with various hematological malignancies, bone marrow failure syndromes, and congenital immune deficiencies. The prevalence of oral complications in both autologous and allogeneic HSCT recipients remains high, despite advances in transplant medicine and in supportive care. Frequently encountered oral complications include mucositis, infections, oral dryness, taste changes, and graft versus host disease in allogeneic HSCT. Oral complications are associated with substantial morbidity and in some cases with increased mortality and may significantly affect quality of life, even many years after HSCT. Inflammatory processes are key in the pathobiology of most oral complications in HSCT recipients. This review article will discuss frequently encountered oral complications associated with HSCT focusing on the inflammatory pathways and inflammatory mediators involved in their pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Shapira MY, Tsirigotis P, Resnick IB, Or R, Abdul-Hai A, Slavin S. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the elderly. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 2007;64(1):49–63. - PubMed
-
- Raber-Durlacher JE, Barasch A, Peterson DE, Lalla RV, Schubert MM, Fibbe WE. Oral complications and management considerations in patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy. Supportive Cancer Therapy. 2004;1:219–229. - PubMed
-
- Barker GJ, Epstein JB, Williams KB, Gorsky M, Raber-Durlacher JE. Current practice and knowledge of oral care for cancer patients: a survey of supportive health care providers. Supportive Care in Cancer. 2005;13(1):32–41. - PubMed
-
- Brennan MT, Elting LS, Spijkervet FKL. Systematic reviews of oral complications from cancer therapies, Oral Care Study Group, MASCC/ISOO: methodology and quality of the literature. Supportive Care in Cancer. 2010;18(8):979–984. - PubMed
-
- Barasch A, Epstein JB. Management of cancer therapy-induced oral mucositis. Dermatologic Therapy. 2011;24(4):424–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

