Radix Astragali Improves Dysregulated Triglyceride Metabolism and Attenuates Macrophage Infiltration in Adipose Tissue in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Male Rats through Activating mTORC1-PPAR γ Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 24817881
- PMCID: PMC4000987
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/189085
Radix Astragali Improves Dysregulated Triglyceride Metabolism and Attenuates Macrophage Infiltration in Adipose Tissue in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Male Rats through Activating mTORC1-PPAR γ Signaling Pathway
Abstract
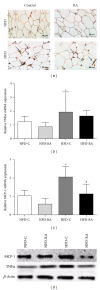
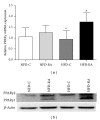
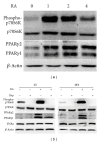
Increased levels of free fatty acids (FFAs) and hypertriglyceridemia are important risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The effective fraction isolated from radix astragali (RA) has been reported to alleviate hypertriglyceridemia. The mechanism of this triglyceride-lowering effect of RA is unclear. Here, we tested whether activation of the mTORC1-PPAR γ signaling pathway is related to the triglyceride-lowering effect of RA. High-fat diet-induced obese (DIO) rats were fed a high-fat diet (40% calories from fat) for 9-10 weeks, and 4 g/kg/d RA was administered by gavage. RA treatment resulted in decreased fasting triglyceride levels, FFA concentrations, and adipocyte size. RA treated rats showed improved triglyceride clearance and fatty acid handling after olive oil overload. RA administration could also decrease macrophage infiltration and expression of MCP-1 and TNF α , but it may also increase the expression of PPAR γ in epididymal adipose tissue from RA treated rats. Consistently, expressions of PPAR γ and phospho-p70S6K were increased in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes treated with RA. Moreover, RA couldnot upregulate the expression of PPAR γ at the presence of rapamycin. In conclusion, the mTORC1-PPAR γ signaling pathway is a potential mechanism through which RA exerts beneficial effects on the disturbance of triglyceride metabolism and dysfunction of adipose tissue in DIO rats.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acer tegmentosum Maxim Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3t3-l1 Adipocytes and Attenuates Lipid Accumulation in Obese Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 7;12(12):3753. doi: 10.3390/nu12123753. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33297378 Free PMC article.
-
Blueberry peel extracts inhibit adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells and reduce high-fat diet-induced obesity.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 25;8(7):e69925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069925. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936120 Free PMC article.
-
Coprinus comatus cap inhibits adipocyte differentiation via regulation of PPARγ and Akt signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 2;9(9):e105809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105809. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25181477 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Obesity and Lipid Lowering Activity of Bauhiniastatin-1 is Mediated Through PPAR-γ/AMPK Expressions in Diet-Induced Obese Rat Model.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 22;12:704074. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.704074. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34366856 Free PMC article.
-
Sparstolonin B inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 15;769:79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.10.050. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26522926
Cited by
-
Exercise alters the molecular pathways of insulin signaling and lipid handling in maternal tissues of obese pregnant mice.Physiol Rep. 2019 Aug;7(16):e14202. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14202. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31466137 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effect of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension diet with usual dietary advice on expression of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma gene in women: A randomized controlled clinical trial.ARYA Atheroscler. 2018 Jan;14(1):24-31. doi: 10.22122/arya.v14i1.1565. ARYA Atheroscler. 2018. PMID: 29942335 Free PMC article.
-
Buyang Huanwu decoction affects gut microbiota and lipid metabolism in a ZDF rat model of co-morbid type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity: An integrated metabolomics analysis.Front Chem. 2022 Nov 9;10:1036380. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1036380. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36438869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eckel RH, Krauss RM. American Heart Association call to action: obesity as a major risk factor for coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1998;97(21):2099–2100. - PubMed
-
- Canoy D, Boekholdt SM, Wareham N, et al. Body fat distribution and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women in the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition in norfolk cohort: a population-based prospective study. Circulation. 2007;116(25):2933–2943. - PubMed
-
- Bardou M, Barkun AN, Martel M. Obesity and colorectal cancer. Gut. 2013;62(6):933–947. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

