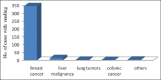
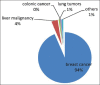
Risk of tumor cell seeding through biopsy and aspiration cytology
- PMID: 24818087
- PMCID: PMC4015162
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-0762.129446
Risk of tumor cell seeding through biopsy and aspiration cytology
Abstract
Cancer cells, besides reproducing uncontrollably, lose cohesiveness and orderliness of normal tissue, invade and get detached from the primary tumor to travel and set up colonies elsewhere. Dislodging neoplastically altered cells from a tumor during biopsy or surgical intervention or during simple procedure like needle aspiration is a possibility because they lack cohesiveness, and they attain the capacity to migrate and colonize. Considering the fact that, every tumor cell, is bathed in interstitial fluid, which drains into the lymphatic system and has an individualized arterial blood supply and venous drainage like any other normal cell in our body, inserting a needle or a knife into a tumor, there is a jeopardy of dislodging a loose tumor cell into either the circulation or into the tissue fluid. Tumor cells are easier to dislodge due to lower cell-to-cell adhesion. This theory with the possibility of seeding of tumor cells is supported by several case studies that have shown that after diagnostic biopsy of a tumor, many patients developed cancer at multiple sites and showed the presence of circulating cancer cells in the blood stream on examination. In this review, we evaluate the risk of exposure to seeding of tumor cells by biopsy and aspiration cytology and provide some suggested practices to prevent tumor cell seeding.
Keywords: Aspiration cytology; biopsy; cancer; metastasis; seeding.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of ultrasound-guided core biopsy versus fine-needle aspiration biopsy in the evaluation of salivary gland lesions.Head Neck. 2013 Nov;35(11):1657-61. doi: 10.1002/hed.23193. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Head Neck. 2013. PMID: 23109044 Review.
-
A case of mucinous carcinoma of the breast in which needle tract seeding was diagnosed by preoperative diagnostic imaging.Breast Cancer. 2011 Oct;18(4):324-7. doi: 10.1007/s12282-009-0151-7. Epub 2009 Aug 22. Breast Cancer. 2011. PMID: 19701680
-
Seeding of tumor cells after fine needle aspiration cytology in benign parotid tumor: a case report and literature review.Laryngoscope. 2008 Feb;118(2):263-5. doi: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e318158f718. Laryngoscope. 2008. PMID: 18030170 Review.
-
Prospective cytological assessment of gastrointestinal luminal fluid acquired during EUS: a potential source of false-positive FNA and needle tract seeding.Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Jun;105(6):1311-8. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.80. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20197762 Clinical Trial.
-
Needle track seeding in renal mass biopsies.Cancer Cytopathol. 2019 Jun;127(6):358-361. doi: 10.1002/cncy.22147. Epub 2019 May 22. Cancer Cytopathol. 2019. PMID: 31116493 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare Abdominal Wall Metastasis following Curative Resection of Gastric Cancer: What Can Be Learned from the Use of Percutaneous Catheters?Case Rep Oncol Med. 2020 May 9;2020:3738798. doi: 10.1155/2020/3738798. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2020. PMID: 32509367 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on Clinical Use of Liquid Biopsy in Colorectal Cancer Screening, Diagnosis, Follow-Up, and Treatment Guidance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 24;9:660924. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.660924. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34150757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of incidental findings from whole-body MRI on the frequency of biopsies and detected malignancies or benign conditions in a general population cohort study.Eur J Epidemiol. 2020 Oct;35(10):925-935. doi: 10.1007/s10654-020-00679-4. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Eur J Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32860149 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution endomicroscopy with a spectrally encoded miniature objective.Biomed Opt Express. 2019 Feb 25;10(3):1432-1445. doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.001432. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2019. PMID: 30891357 Free PMC article.
-
Association between biopsy method and development of peritoneal metastases in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma.HPB (Oxford). 2022 Jun;24(6):942-949. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2021.11.001. Epub 2021 Nov 10. HPB (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 34844860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biopsy and surgery can spread cancer. Dr. Vincent Gammill Center for the Study of Natural Oncology (CSNO) Solana Beach, California. Available from: www.healingcancernaturally.com/biopsies-surgery-spread-cancer.html .
-
- Moran P. Cancer treatment watch. Do biopsies or surgical treatment spread cancer? Available from: http://www.cancertreatmentwatch.org/general/biopsiess.html .
-
- Orell SR, Sterrette GF, Whitaker D. 4th ed. New Delhi: Churchill Livingstone, Published by Elsevier, Reed Elsevier India Private Ltd; 2005. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology-Text Book; pp. 1–8.
-
- Hansen NM, Ye X, Grube BJ, Giuliano AE. Manipulation of the primary breast tumor and the incidence of sentinel node metastases from invasive breast cancer. Arch Surg. 2004;139:634–9. - PubMed
-
- Dangers of cancer spread from a biopsy. [Last Accessed in 2013 Jun 5]. Available from: http://www.karlloren.com/biopsy/p46.htm .
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical