Characterization of small interfering RNAs derived from Sugarcane mosaic virus in infected maize plants by deep sequencing
- PMID: 24819114
- PMCID: PMC4018358
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097013
Characterization of small interfering RNAs derived from Sugarcane mosaic virus in infected maize plants by deep sequencing
Abstract
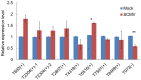
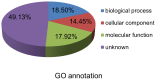
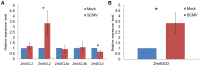
RNA silencing is a conserved surveillance mechanism against viruses in plants. It is mediated by Dicer-like (DCL) proteins producing small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which guide specific Argonaute (AGO)-containing complexes to inactivate viral genomes and may promote the silencing of host mRNAs. In this study, we obtained the profile of virus-derived siRNAs (vsiRNAs) from Sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV) in infected maize (Zea mays L.) plants by deep sequencing. Our data showed that vsiRNAs which derived almost equally from sense and antisense SCMV RNA strands accumulated preferentially as 21- and 22-nucleotide (nt) species and had an adenosine bias at the 5'-terminus. The single-nucleotide resolution maps revealed that vsiRNAs were almost continuously but heterogeneously distributed throughout the SCMV genome and the hotspots of sense and antisense strands were mainly distributed in the HC-Pro coding region. Moreover, dozens of host transcripts targeted by vsiRNAs were predicted, several of which encode putative proteins involved in ribosome biogenesis and in biotic and abiotic stresses. We also found that ZmDCL2 mRNAs were up-regulated in SCMV-infected maize plants, which may be the cause of abundant 22-nt vsiRNAs production. However, ZmDCL4 mRNAs were down-regulated slightly regardless of the most abundant 21-nt vsiRNAs. Our results also showed that SCMV infection induced the accumulation of AGO2 mRNAs, which may indicate a role for AGO2 in antiviral defense. To our knowledge, this is the first report on vsiRNAs in maize plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic infection of two viruses MCMV and SCMV increases the accumulations of both MCMV and MCMV-derived siRNAs in maize.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 11;6:20520. doi: 10.1038/srep20520. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26864602 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of small interfering RNAs derived from Rice black streaked dwarf virus in infected maize plants by deep sequencing.Virus Res. 2017 Jan 15;228:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27888127
-
Virus-Derived Small Interfering RNAs Affect the Accumulations of Viral and Host Transcripts in Maize.Viruses. 2018 Nov 23;10(12):664. doi: 10.3390/v10120664. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30477197 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis, Function, and Applications of Virus-Derived Small RNAs in Plants.Front Microbiol. 2015 Nov 9;6:1237. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01237. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26617580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of virus-derived small interfering RNAs in RNA silencing in plants.Sci China Life Sci. 2012 Feb;55(2):119-25. doi: 10.1007/s11427-012-4281-3. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Sci China Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22415682 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Hibiscus Latent Fort Pierce Virus-Derived siRNAs in Infected Hibiscus rosa-sinensis in China.Plant Pathol J. 2020 Dec 1;36(6):618-627. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.09.2020.0169. Plant Pathol J. 2020. PMID: 33312097 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of small RNAs derived from tomato brown rugose fruit virus in infected Solanum lycopersicum plants by deep sequencing.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 30;15:1504861. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1504861. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39949351 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Functions of Small RNAs in Different Plant-Pathogen Communications.Front Microbiol. 2016 Oct 4;7:1552. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01552. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27757103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different Virus-Derived siRNAs Profiles between Leaves and Fruits in Cucumber Green Mottle Mosaic Virus-Infected Lagenaria siceraria Plants.Front Microbiol. 2016 Nov 9;7:1797. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01797. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27881977 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing reveals the first fabavirus infecting peach.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 12;7(1):11329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11743-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28900201 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC (1999) A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286: 950–952. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP (2000) RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101: 25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

