"Greenlight study": a controlled trial of low-literacy, early childhood obesity prevention
- PMID: 24819570
- PMCID: PMC4035594
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2013-3867
"Greenlight study": a controlled trial of low-literacy, early childhood obesity prevention
Abstract
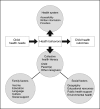
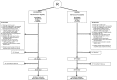
Children who become overweight by age 2 years have significantly greater risks of long-term health problems, and children in low-income communities, where rates of low adult literacy are highest, are at increased risk of developing obesity. The objective of the Greenlight Intervention Study is to assess the effectiveness of a low-literacy, primary-care intervention on the reduction of early childhood obesity. At 4 primary-care pediatric residency training sites across the US, 865 infant-parent dyads were enrolled at the 2-month well-child checkup and are being followed through the 24-month well-child checkup. Two sites were randomly assigned to the intervention, and the other sites were assigned to an attention-control arm, implementing the American Academy of Pediatrics' The Injury Prevention Program. The intervention consists of an interactive educational toolkit, including low-literacy materials designed for use during well-child visits, and a clinician-centered curriculum for providing low-literacy guidance on obesity prevention. The study is powered to detect a 10% difference in the number of children overweight (BMI > 85%) at 24 months. Other outcome measures include observed physician-parent communication, as well as parent-reported information on child dietary intake, physical activity, and injury-prevention behaviors. The study is designed to inform evidence-based standards for early childhood obesity prevention, and more generally to inform optimal approaches for low-literacy messages and health literacy training in primary preventive care. This article describes the conceptual model, study design, intervention content, and baseline characteristics of the study population.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01040897.
Keywords: early childhood; health literacy; injury prevention; obesity prevention; primary care; resident education.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Figures




References
-
- Barlow SE. Expert Committee. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Pediatrics. 2007;120(suppl 4):S164–S192 - PubMed
-
- Sherry B, Mei Z, Scanlon KS, Mokdad AH, Grummer-Strawn LM. Trends in state-specific prevalence of overweight and underweight in 2- through 4-year-old children from low-income families from 1989 through 2000. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004;158(12):1116–1124 - PubMed
-
- Suminski RR, Poston WS, Jackson AS, Foreyt JP. Early identification of Mexican American children who are at risk for becoming obese. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23(8):823–829 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

