Identification and characterization of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of β-catenin signaling
- PMID: 24819961
- PMCID: PMC4076560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.04.002
Identification and characterization of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of β-catenin signaling
Abstract
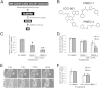
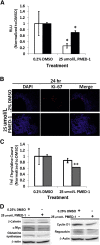
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the third most common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, lacks effective medical therapy. Large subsets of HCC demonstrate Wnt/β-catenin activation, making this an attractive therapeutic target. We report strategy and characterization of a novel small-molecule inhibitor, ICG-001, known to affect Wnt signaling by disrupting β-catenin-CREB binding protein interactions. We queried the ZINC online database for structural similarity to ICG-001 and identified PMED-1 as the lead compound, with ≥70% similarity to ICG-001. PMED-1 significantly reduced β-catenin activity in hepatoblastoma and several HCC cells, as determined by TOPflash reporter assay, with an IC50 ranging from 4.87 to 32 μmol/L. Although no toxicity was observed in primary human hepatocytes, PMED-1 inhibited Wnt target expression in HCC cells, including those with CTNNB1 mutations, and impaired cell proliferation and viability. PMED-1 treatment decreased β-catenin-CREB binding protein interactions without affecting total β-catenin levels or activity of other common kinases. PMED-1 treatment of Tg(OTM:d2EGFP) zebrafish expressing GFP under the β-catenin/Tcf reporter led to a notable decrease in β-catenin activity. The PMED effect on β-catenin signaling lasted from 12 to 24 hours in vitro and 6 to 15 hours in vivo. Thus, using a rapid and cost-effective computational methodology, we have identified a novel and specific small-molecule inhibitor of Wnt signaling that may have implications for HCC treatment.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Ferlay J., Shin H.R., Bray F., Forman D., Mathers C., Parkin D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Fortune B.E., Umman V., Gilliland T., Emre S. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a surgical perspective. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013;47(Suppl):S37–S42. - PubMed
-
- Imamura H., Matsuyama Y., Tanaka E., Ohkubo T., Hasegawa K., Miyagawa S., Sugawara Y., Minagawa M., Takayama T., Kawasaki S., Makuuchi M. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003;38:200–207. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K., Kono N., Ono A., Osuga Y., Kiyokawa H., Mineo I., Matsuda Y., Miyoshi S., Kawata S., Minami Y., Moriwaki K., Tarui S. Transcatheter arterial chemo-embolization for humoral hypercalcemia of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1988;23:29–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

