Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of morinidazole: uptake transporter-mediated renal clearance of the conjugated metabolites
- PMID: 24820074
- PMCID: PMC4068547
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02414-14
Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of morinidazole: uptake transporter-mediated renal clearance of the conjugated metabolites
Abstract
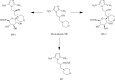
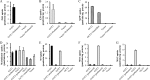
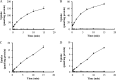
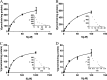
Morinidazole is a novel 5-nitroimidazole antimicrobial drug that undergoes extensive metabolism in humans via N(+)-glucuronidation (N(+)-glucuronide of S-morinidazole [M8-1] and N(+)-glucuronide of R-morinidazole [M8-2]) and sulfation (sulfate conjugate of morinidazole [M7]). Our objectives were to assess the effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics (PK) of morinidazole and to elucidate the potential mechanisms. In this parallel-group study, healthy subjects and patients with severe renal impairment received an intravenous infusion of 500 mg of morinidazole. Plasma and urine samples were collected and analyzed. The areas under the plasma concentration-time curves (AUC) for M7, M8-1, and M8-2 were 15.1, 20.4, and 17.4 times higher, respectively, in patients with severe renal impairment than in healthy subjects, while the AUC for morinidazole was 1.5 times higher. The urinary recovery of the major metabolites was not significantly different between the two groups over 0 to 48 h, but the renal clearances of M7, M8-1, and M8-2 in patients were 85.3%, 92.5%, and 92.2% lower, respectively. In vitro transporter studies revealed that M7 is a substrate for organic anion transporter 1 (OAT1) and OAT3 (Km = 28.6 and 54.0 μM, respectively). Only OAT3 transported M8-1 and M8-2. Morinidazole was not a substrate for the transporter-transfected cells examined. These results revealed that the function or activity of renal uptake transporters might be impaired in patients with severe renal impairment, which accounted for dramatically increased plasma exposure and reduced renal clearance of the conjugated metabolites of morinidazole, the substrates of renal transporters in patients. It will help clinicians to adjust the dose in patients with severe renal impairment and to predict possible transporter-based drug-drug interactions.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lv A. 2008. Usage of alpha-(morpholin-1-base) methyl-2-methyl-5-azathio-1-alcohol in preparation of anti-trichomoniasis and anti-ameba medicines. China patent ZL 200510134254.3
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

