Inhibition of aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib by zinc: reversal of amikacin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli by a zinc ionophore
- PMID: 24820083
- PMCID: PMC4068593
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00129-14
Inhibition of aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib by zinc: reversal of amikacin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli by a zinc ionophore
Abstract
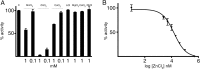
In vitro activity of the aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib [AAC(6')-Ib] was inhibited by ZnCl2 with a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 15 μM. Growth of Acinetobacter baumannii or Escherichia coli harboring aac(6')-Ib in cultures containing 8 μg/ml amikacin was significantly inhibited by the addition of 2 μM Zn(2+) in complex with the ionophore pyrithione (ZnPT).
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amikacin potentiator activity of zinc complexed to a pyrithione derivative with enhanced solubility.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 7;12(1):285. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04724-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 34997203 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib-mediated amikacin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae by zinc and copper pyrithione.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Sep;59(9):5851-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01106-15. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26169410 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib-mediated amikacin resistance by zinc complexed with clioquinol, an ionophore active against tumors and neurodegenerative diseases.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Feb;51(2):271-273. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 28782708 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inhibiting Amikacin Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria with Cadmium and Pyrithione.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Jul 16;82(9):389. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04372-1. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40668405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amikacin: Uses, Resistance, and Prospects for Inhibition.Molecules. 2017 Dec 19;22(12):2267. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122267. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29257114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Potential Virulence Factors in the Model Strain Acinetobacter baumannii A118.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 23;10:1599. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01599. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31396168 Free PMC article.
-
Small Klebsiella pneumoniae Plasmids: Neglected Contributors to Antibiotic Resistance.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 20;10:2182. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02182. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31616398 Free PMC article.
-
A Drug Repositioning Approach Reveals that Streptococcus mutans Is Susceptible to a Diverse Range of Established Antimicrobials and Nonantibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Dec 21;62(1):e01674-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01674-17. Print 2018 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 29061736 Free PMC article.
-
Collateral Sensitivity Interactions between Antibiotics Depend on Local Abiotic Conditions.mSystems. 2021 Dec 21;6(6):e0105521. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.01055-21. Epub 2021 Nov 30. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34846167 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome of the Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strain A155 Clinical Isolate.Genome Announc. 2015 Mar 26;3(2):e00212-15. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00212-15. Genome Announc. 2015. PMID: 25814610 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

