Patterns of failure after radical surgery among patients with thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: implications for the clinical target volume design of postoperative radiotherapy
- PMID: 24820177
- PMCID: PMC4018255
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097225
Patterns of failure after radical surgery among patients with thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: implications for the clinical target volume design of postoperative radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: This study evaluated patterns of treatment failure (especially locoregional failure; LRF) after radical esophagectomy and proposes a clinical target volume (CTV) for postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) among patients with thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
Methods: All patients who were followed up in our center after radical esophagectomy between 2007 and 2011 were retrospectively enrolled. The patterns of first discovered failure were assessed, and LRFs (including anastomotic and regional lymph node recurrences) were evaluated to determine whether our proposed PORT CTV encompassed these areas. The clinicopathologic factors predictive of lymphatic recurrence type were analyzed.
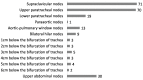
Results: Of the 414 patients who underwent surgery and were followed up over the study, 207 experienced recurrent or metastatic diseases. The median time to progression was 11.0 months. Of the 173 patients with locoregional recurrence, nodal failure recurred in 160; supraclavicular and superior mediastinal lymph nodes had the highest metastasis rates. All 233 recurrent sites across the 160 patients were located in a standard CTV area, including the bilateral supraclavicular areas, the entire mediastinum, and the left gastric lymphatic drainage region. A total of 203 sites (87.2%) were located in either the bilateral supraclavicular areas or the entire mediastinum, and 185 sites (79.4%) were located in either the bilateral supraclavicular areas or the upper mediastinum. A multivariate analysis revealed the lymph node metastatic ratio (LNMR) and tumor differentiation were risk factors for nodal failure.
Conclusions: Locoregional recurrence (especially lymph node recurrence) was the most common and potentially preventable type of initial treatment failure after curative surgery among patients with thoracic esophageal SCC. The proposed PORT CTV covered most LRF sites. The lymphatic drainage regions for PORT are selective, and the supraclavicular and superior mediastinal areas should be considered. However, the value of PORT and the extent of CTV should be investigated in further prospective studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mirinezhad SK, Somi MH, Seyednezhad F, Jangjoo AG, Ghojazadeh M, et al. (2013) Survival in patients treated with definitive chemo-radiotherapy for non-metastatic esophageal cancer in north- west iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14: 1677–1680. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa S, Kanda T, Kosugi S, Ohashi M, Suzuki T, et al. (2004) Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus after extended radical esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 198: 205–211. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Wang Z, Liu XY, Liu FY (2007) Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma in the middle thoracic esophagus after modified Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy. World J Surg 31: 1107–1114. - PubMed
-
- van Hagen P, Wijnhoven BP, Nafteux P, Moons J, Haustermans K, et al. (2013) Recurrence pattern in patients with a pathologically complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and surgery for oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg 100: 267–273. - PubMed
-
- van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ, Steyerberg EW, van Berge HM, et al. (2012) Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med 366: 2074–2084. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials