Core binding factor beta (Cbfβ) controls the balance of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation by upregulating Indian hedgehog (Ihh) expression and inhibiting parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor (PPR) expression in postnatal cartilage and bone formation
- PMID: 24821091
- PMCID: PMC4644666
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.2275
Core binding factor beta (Cbfβ) controls the balance of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation by upregulating Indian hedgehog (Ihh) expression and inhibiting parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor (PPR) expression in postnatal cartilage and bone formation
Abstract
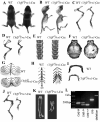
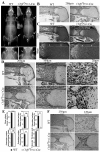
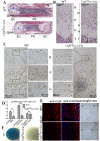
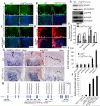
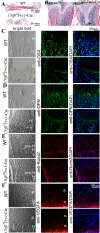
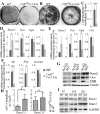
Core binding factor beta (Cbfβ) is essential for embryonic bone morphogenesis. Yet the mechanisms by which Cbfβ regulates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation as well as postnatal cartilage and bone formation remain unclear. Hence, using paired-related homeobox transcription factor 1-Cre (Prx1-Cre) mice, mesenchymal stem cell-specific Cbfβ-deficient (Cbfβ(f/f) Prx1-Cre) mice were generated to study the role of Cbfβ in postnatal cartilage and bone development. These mutant mice survived to adulthood but exhibited severe sternum and limb malformations. Sternum ossification was largely delayed in the Cbfβ(f/f) Prx1-Cre mice and the xiphoid process was noncalcified and enlarged. In newborn and 7-day-old Cbfβ(f/f) Prx1-Cre mice, the resting zone was dramatically elongated, the proliferation zone and hypertrophic zone of the growth plates were drastically shortened and disorganized, and trabecular bone formation was reduced. Moreover, in 1-month-old Cbfβ(f/f) Prx1-Cre mice, the growth plates were severely deformed and trabecular bone was almost absent. In addition, Cbfβ deficiency impaired intramembranous bone formation both in vivo and in vitro. Interestingly, although the expression of Indian hedgehog (Ihh) was largely reduced, the expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) receptor (PPR) was dramatically increased in the Cbfβ(f/f) Prx1-Cre growth plate, indicating that that Cbfβ deficiency disrupted the Ihh-PTHrP negative regulatory loop. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis and promoter luciferase assay demonstrated that the Runx/Cbfβ complex binds putative Runx-binding sites of the Ihh promoter regions, and also the Runx/Cbfβ complex directly upregulates Ihh expression at the transcriptional level. Consistently, the expressions of Ihh target genes, including CyclinD1, Ptc, and Pthlh, were downregulated in Cbfβ-deficient chondrocytes. Taken together, our study reveals not only that Cbfβ is essential for chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation for the growth and maintenance of the skeleton in postnatal mice, but also that it functions in upregulating Ihh expression to promoter chondrocyte proliferation and osteoblast differentiation, and inhibiting PPR expression to enhance chondrocyte differentiation.
Keywords: DEVELOPMENT; GENETIC ANIMAL MODELS; GROWTH PLATE; INDIAN HEDGEHOG; OSTEOBLASTS; SIGNALING PATHWAYS.
© 2014 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures
References
-
- Speck NA, Terryl S. A new transcription factor family associated with human leukemias. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1995;5(3-4):337–64. - PubMed
-
- Levanon D, Negreanu V, Bernstein Y, Bar-Am I, Avivi L, Groner Y. AML1, AML2, and AML3, the human members of the runt domain gene-family: cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal localization. Genomics. 1994;23(2):425–32. - PubMed
-
- Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A, Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M, Sato M, Okamoto R, Kitamura Y, Yoshiki S, Kishimoto T. Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell. 1997;89(5):755–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

